Biomarkers Predictive of Response to Thiopurine Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 32064265
- PMCID: PMC7000528
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00008
Biomarkers Predictive of Response to Thiopurine Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
The complex nature of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) often results in treatment failure for many patients. With some patients cycling through multiple therapies before achieving a sustained period of remission, the ability to predict a patient's response to therapeutics could decrease the time from active disease to clinical remission and mucosal healing. The prospect of such individualized treatment of IBD would be aided by accurate biomarkers, both fecal and serological, which have to date shown value as indicators of IBD activity. Here we review the utility of generic biomarkers for inflammation or mucosal healing, such as calprotectin, C-reactive protein (CRP), and fecal hemoglobin (fHb) as predictors of response to treatment of IBD. We further provide a deeper insight into the utility of monitoring the thiopurine treatment by thiopurine metabolites or alternative hematologic parameters. In light of multiple recent publications of biomarkers and biological therapy, our focus in this review is predicting response to thiopurine treatment only, that is, Azathioprine and 6-Mercaptopurine.
Keywords: 6-mercaptopurine; Crohn's disease; azathioprine; intestinal inflammation; outcome; predictors; thiopurine; ulcerative colitis.
Copyright © 2020 Cornish, Wirthgen and Däbritz.
Figures
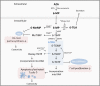
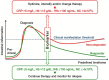
References
-
- Cornillie F, Hanauer SB, Diamond RH, Wang J, Tang KL, Xu Z, et al. Postinduction serum infliximab trough level and decrease of C-reactive protein level are associated with durable sustained response to infliximab: a retrospective analysis of the ACCENT I trial. Gut. (2014) 63:1721–7. 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304094 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

