Pericardial Tamponade After Systemic Alteplase in Stroke and Emergent Reversal With Tranexamic Acid
- PMID: 32064426
- PMCID: PMC7012568
- DOI: 10.5811/cpcem.2019.10.44369
Pericardial Tamponade After Systemic Alteplase in Stroke and Emergent Reversal With Tranexamic Acid
Abstract
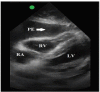
Alteplase, or tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), lyses clots by enhancing activation of plasminogen to plasmin. Conversely, tranexamic acid (TXA) functions by inhibiting the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, which inhibits fibrinolysis. TXA has proven safe and effective in major bleeding with various etiologies. A 76-year-old male developed acute ischemic stroke symptoms. Systemic alteplase was administered and he showed clinical improvement. Shortly thereafter, the patient became hypotensive and lost pulses. Point-of-care ultrasound revealed cardiac tamponade. TXA was immediately given to inhibit fibrinolysis since cryoprecipitate and blood products were not immediately available. Pericardiocentesis was performed and successfully removed 200 milliliters of blood with return of pulses. Clinicians must consider TXA as a rapidly accessible antagonist of tPA's fibrinolytic effects.
Copyright: © 2020 Romero et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: By the CPC-EM article submission agreement, all authors are required to disclose all affiliations, funding sources and financial or management relationships that could be perceived as potential sources of bias. The authors disclosed none.
Figures
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Mutner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e227. - PubMed
-
- Hensen H, Spaander F, Bax M, et al. Fatal hemopericardium after intravenous recombinant transplasminogeen activator (rt-PA) for acute ischemic stroke. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(12):2462.e5–6. - PubMed
-
- Dhand A, Nakagawa K, Nagpal S, et al. Cardiac rupture after intravenous t-PA administration in acute ischemic stroke. Neurocrit Care. 2010;13(2):261–2. - PubMed
-
- De Silva DA, Manzano JJ, Chang HM, et al. Reconsidering recent myocardial infarction as a contraindication for IV stroke thromolysis. Neurology. 2011;76(21):1838–40. - PubMed
