Concurrent use of rabacfosadine and L-asparaginase for relapsed or refractory multicentric lymphoma in dogs
- PMID: 32064697
- PMCID: PMC7096650
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.15723
Concurrent use of rabacfosadine and L-asparaginase for relapsed or refractory multicentric lymphoma in dogs
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Concurrent use of rabacfosadine and L-asparaginase for relapsed or refractory multicentric lymphoma in dogs.J Vet Intern Med. 2020 May;34(3):1358. doi: 10.1111/jvim.15786. Epub 2020 Apr 27. J Vet Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32463988 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Rabacfosadine (RAB), a novel antineoplastic agent conditionally licensed for the treatment of lymphoma in dogs, is efficacious in both naïve and previously treated dogs. Its use in combination with L-asparaginase (L-ASP) has not been studied.
Hypothesis/objectives: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of L-ASP given concurrently with RAB in dogs with relapsed multicentric lymphoma.
Animals: Fifty-two dogs with relapse of lymphoma after treatment with at least 1 doxorubicin-based chemotherapy protocol.
Methods: Open-label, multicenter, prospective single-arm clinical trial. Dogs were treated with RAB at 1.0 mg/kg IV every 21 days for up to a total of 5 doses. L-asparaginase was administered at 400 IU/kg SQ concurrently with the first 2 treatments of RAB.
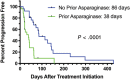
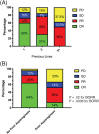
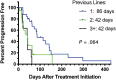
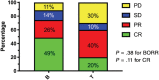
Results: The overall response rate (ORR) for all dogs was 67%, with 19 dogs (41%) achieving a complete response (CR). The median progression-free survival time (MPFS) was 63 days (range 5-428 days). Dogs experiencing a CR as their best response had an MPFS of 144 days (range 44-428 days). Adverse events were similar to previous studies evaluating single agent RAB. Failure to achieve a CR and having previously received L-ASP were negative prognostic factors on multivariate analysis.
Conclusions and clinical importance: Concurrent RAB/L-ASP appears to be both efficacious and safe for treating relapsed multicentric lymphoma in dogs. Adverse events were most often mild and no unexpected toxicoses were observed.
Keywords: GS-9219; Tanovea; asparaginase; chemotherapy; dog; guanine; lymphosarcoma.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Douglas H. Thamm is a consultant for and shareholder in VetDC. Karri Meleo, Gerald S. Post, Kathryn R. Vickery, David M. Vail, and Philip J. Bergman are members of VetDC's Clinical Advisory Board.
Figures

References
-
- Zemann BI, Moore AS, William RM, et al. A combination chemotherapy protocol (VELCAP‐L) for dogs with lymphoma. J Vet Intern Med. 1998;12:465‐470. - PubMed
-
- Vail DM, Thamm DH, Reiser H, et al. Assessment of GS‐9219 in a pet dog model of non‐Hodgkin's lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(10):3503‐3510. - PubMed
-
- Reiser H, Wang J, Chong L, et al. GS‐9219—a novel acyclic nucleotide analogue with potent antineoplastic activity in dogs with spontaneous non‐Hodgkin's lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(9):2824‐2832. - PubMed
-
- Saba CF, Vickery KR, Clifford CA, et al. Rabacfosadine for relapsed canine B‐cell lymphoma: efficacy and adverse event profiles of 2 different doses. Vet Comp Oncol. 2017;16(1):E76‐E82. - PubMed
-
- Panosyan EH, Grigoryan RS, Avramis IA, et al. Deamination of glutamine is a prerequisite for optimal asparagine deamination by asparaginases in vivo (CCG‐1961). Anticancer Res. 2004;24(2C):1121‐1125. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

