Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients: implication of multiple shedding routes
- PMID: 32065057
- PMCID: PMC7048229
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1729071
Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients: implication of multiple shedding routes
Abstract
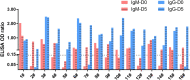
In December 2019, a novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) caused an outbreak in Wuhan, China, and soon spread to other parts of the world. It was believed that 2019-nCoV was transmitted through respiratory tract and then induced pneumonia, thus molecular diagnosis based on oral swabs was used for confirmation of this disease. Likewise, patient will be released upon two times of negative detection from oral swabs. However, many coronaviruses can also be transmitted through oral-fecal route by infecting intestines. Whether 2019-nCoV infected patients also carry virus in other organs like intestine need to be tested. We conducted investigation on patients in a local hospital who were infected with this virus. We found the presence of 2019-nCoV in anal swabs and blood as well, and more anal swab positives than oral swab positives in a later stage of infection, suggesting shedding and thereby transmitted through oral-fecal route. We also showed serology test can improve detection positive rate thus should be used in future epidemiology. Our report provides a cautionary warning that 2019-nCoV may be shed through multiple routes.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; Wuhan pneumonia; epidemiology; intestine; swabs.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Comment in
-
Atypical pneumonia diagnosed as coronavirus disease 2019 by a serologic test (patient -1 in Poland).Pol Arch Intern Med. 2020 May 29;130(5):444-445. doi: 10.20452/pamw.15313. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32329977 No abstract available.
-
A family cluster of COVID-19 involving an asymptomatic case with persistently positive SARS-CoV-2 in anal swabs.Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020 Nov-Dec;38:101745. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101745. Epub 2020 May 16. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33353595 No abstract available.
References
-
- W. H. Organization . WHO Press Statement Related to the Novel Coronavirus Situation, 2019).
-
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, et al. Discovery of a novel coronavirus associated with the recent pneumonia outbreak in humans and its potential bat origin. BioRxiv. 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical