Enterohemorrhagic E. coli effector NleL disrupts host NF-κB signaling by targeting multiple host proteins
- PMID: 32065237
- PMCID: PMC7232126
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjaa003
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli effector NleL disrupts host NF-κB signaling by targeting multiple host proteins
Figures
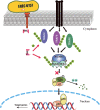
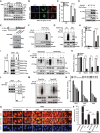
References
-
- Kobayashi T., Walsh M.C., and Choi Y. (2004). The role of TRAF6 in signal transduction and the immune response. Microbes Infect. 6, 1333–1338. - PubMed
-
- Mead P.S., and Griffin P.M. (1998). Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet 352, 1207–1212. - PubMed
-
- Neish A.S., and Naumann M. (2011). Microbial-induced immunomodulation by targeting the NF-κB system. Trends Microbiol. 19, 596–605. - PubMed

