Noninvasive indices for predicting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 32066395
- PMCID: PMC7027038
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-020-01718-8
Noninvasive indices for predicting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Data on clinical characteristics of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are scarce. We investigated the clinical features and risk factors of NAFLD using noninvasive serum markers in CKD patients and attempted the temporal validation of a predictive model for CKD based on NAFLD.
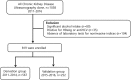
Methods: This retrospective cross-sectional study was conducted in a single tertiary center. We enrolled 819 CKD patients and evaluated the predictive performance of relevant clinical and laboratory markers for the presence of NAFLD in both derivation (data from 2011 to 2014, n = 567) and validation (data from 2015 to 2016, n = 252) groups.
Results: In the derivation group, NAFLD was observed in 89 patients (15.7%; mean body mass index (BMI), 24.6 kg/m2; median estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), 28.0 ml/min). BMI, hemoglobin, serum alanine aminotransferase, eGFR, and triglyceride-glucose index were used to derive a prediction model for the presence of NAFLD. Using the cutoff value of 0.146, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) for the prediction of NAFLD was 0.850. In the validation group, NAFLD was observed in 51 patients (20.2%; mean BMI, 25.4 kg/m2; median eGFR, 36.0 ml/min). Using the same prediction model and cutoff value, the AUROC was 0.842. NAFLD prevalence in CKD patients was comparable to that in the general population, increasing over time.
Conclusions: Our model using BMI, renal function, triglyceride-glucose index, serum alanine aminotransferase, and hemoglobin accurately predicted the presence of NAFLD in CKD patients.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Noninvasive markers; Prediction model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- McCullough K, Sharma P, Ali T, Khan I, Smith WC, MacLeod A, Black C. Measuring the population burden of chronic kidney disease: a systematic literature review of the estimated prevalence of impaired kidney function. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;27(5):1812–1821. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr547. - DOI - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) and European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64(6):1388–402. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, Charlton M, Sanyal AJ. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatol. 2012;55(6):2005–2023. doi: 10.1002/hep.25762. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

