Evaluation and Treatment of Acute Rejection in Kidney Allografts
- PMID: 32066593
- PMCID: PMC7057293
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.11991019
Evaluation and Treatment of Acute Rejection in Kidney Allografts
Abstract
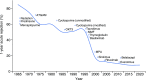
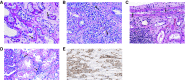
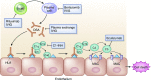
Advances in immunosuppressive therapy have drastically improved acute rejection rates in kidney transplant recipients over the past five decades. Nevertheless, it should remain high on any differential diagnosis of unexplained graft dysfunction because of the potential negative effect on graft longevity. Understanding the pre- and post-transplant risk factors for acute rejection can help estimate the probability of immunologic graft damage, and accurate identification of the type and severity of acute rejection will guide appropriate treatment. Tissue biopsy remains the gold standard for evaluating immunologic graft damage, and the histologic definition of acute rejection has evolved in recent years. Intravenous steroids and T cell depletion remain the standard therapy for T cell-mediated rejection and are effective in reversing most cases. Plasma exchange and intravenous Ig, with or without rituximab, are most commonly used for the treatment of antibody-mediated rejection and several newer agents have recently been investigated for severe cases. This review aims to provide the general nephrologist caring for transplant recipients with an approach to immunologic risk assessment and a summary of recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of acute graft rejection.
Keywords: Immunology and pathology; acute allograft rejection; allografts; antibodies; biopsy; differential diagnosis; graft rejection; humans; immunosuppression; intravenous immunoglobulins; kidney transplantation; longevity; nephrologists; plasma exchange; plasmapheresis; renal transplantation; risk assessment; risk factors; rituximab; t-lymphocytes; transplant recipients.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Zand MS: Immunosuppression and immune monitoring after renal transplantation. Semin Dial 18: 511–519, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Vernerey D, Duong-Van-Huyen JP, Suberbielle C, Anglicheau D, Vérine J, Beuscart T, Nochy D, Bruneval P, Charron D, Delahousse M, Empana JP, Hill GS, Glotz D, Legendre C, Jouven X: Antibody-mediated vascular rejection of kidney allografts: A population-based study. Lancet 381: 313–319, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Bouatou Y, Viglietti D, Pievani D, Louis K, Duong Van Huyen JP, Rabant M, Aubert O, Taupin JL, Glotz D, Legendre C, Loupy A, Lefaucheur C: Response to treatment and long-term outcomes in kidney transplant recipients with acute T cell-mediated rejection. Am J Transplant 19: 1972–1988, 2019 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

