Advances in non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis
- PMID: 32066623
- PMCID: PMC7945956
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317593
Advances in non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis
Abstract
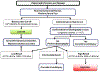
Liver fibrosis should be assessed in all individuals with chronic liver disease as it predicts the risk of future liver-related morbidity and thus need for treatment, monitoring and surveillance. Non-invasive fibrosis tests (NITs) overcome many limitations of liver biopsy and are now routinely incorporated into specialist clinical practice. Simple serum-based tests (eg, Fibrosis Score 4, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Fibrosis Score) consist of readily available biochemical surrogates and clinical risk factors for liver fibrosis (eg, age and sex). These have been extensively validated across a spectrum of chronic liver diseases, however, tend to be less accurate than more 'complex' serum tests, which incorporate direct measures of fibrogenesis or fibrolysis (eg, hyaluronic acid, N-terminal propeptide of type three collagen). Elastography methods quantify liver stiffness as a marker of fibrosis and are more accurate than simple serum NITs, however, suffer increasing rates of unreliability with increasing obesity. MR elastography appears more accurate than sonographic elastography and is not significantly impacted by obesity but is costly with limited availability. NITs are valuable for excluding advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis, however, are not sufficiently predictive when used in isolation. Combining serum and elastography techniques increases diagnostic accuracy and can be used as screening and confirmatory tests, respectively. Unfortunately, NITs have not yet been demonstrated to accurately reflect fibrosis change in response to treatment, limiting their role in disease monitoring. However, recent studies have demonstrated lipidomic, proteomic and gut microbiome profiles as well as microRNA signatures to be promising techniques for fibrosis assessment in the future.
Keywords: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; chronic liver disease; cirrhosis; elastography; serum biomarkers.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: LAA holds patents for Hepascore and his employer (University of Western Australia) has a licensing agreement with Quest Diagnostics. RL serves as a consultant or advisory board member for Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bird Rock Bio, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myer Squibb, Celgene, Cirius, CohBar, Conatus, Eli Lilly, Galmed, Gemphire, Gilead, Glympse bio, GNI, GRI Bio, Intercept, Ionis, Janssen, Merck, Metacrine, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Prometheus, Sanofi, Siemens, and Viking Therapeutics. In addition, his institution has received grant support from Allergan, BoehringerIngelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cirius, Eli Lilly and Company, Galectin Therapeutics, Galmed Pharmaceuticals, GE, Genfit, Gilead, Intercept, Grail, Janssen, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Merck, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, NuSirt, Pfizer, pH Pharma, Prometheus, and Siemens. He is also cofounder of Liponexus.
Figures
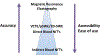
Comment in
-
Non-invasive diagnosis of patients with 'at-risk' NAFLD : only fibrosis counts?Gut. 2020 Jul;69(7):1164-1165. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320785. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Gut. 2020. PMID: 32220903 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zoubek ME, Trautwein C, Strnad P. Reversal of liver fibrosis: from fiction to reality. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2017;31:129–41. - PubMed
-
- Huang Y, de Boer WB, Adams LA, et al. Image analysis of liver biopsy samples measures fibrosis and predicts clinical outcome. J Hepatol 2014;61:22–7. - PubMed
-
- Sebastiani G, Castera L, Halfon P, et al. The impact of liver disease aetiology and the stages of hepatic fibrosis on the performance of non-invasive fibrosis biomarkers: an international study of 2411 cases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011;34:1202–16. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, George J, Bugianesi E, et al. Complex non-invasive fibrosis models are more accurate than simple models in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;26:1536–43. - PubMed
-
- Bertrais S, Boursier J, Ducancelle A, et al. Prognostic durability of liver fibrosis tests and improvement in predictive performance for mortality by combining tests. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;32:1240–9. - PubMed
