Respiratory outcomes with the use of a lower custom fit genioglossal-effecting oral appliance
- PMID: 32067401
- PMCID: PMC7025983
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.254
Respiratory outcomes with the use of a lower custom fit genioglossal-effecting oral appliance
Abstract
Objective: Sleep apnea research cites that an oral appliance, which places the mandible in a more forward position and the genioglossus (tongue muscle) on the floor of the mouth, improves aspects of the pharyngeal opening. Exercise science research has cited improvements in airway dynamics and physiological variables with oral appliance use during exercise. Thus, the purpose of this study was to design an oral appliance that would act on the genioglossus and determine if there were effects on respiratory parameters while exercising.
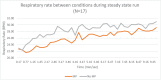
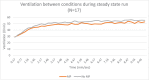
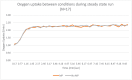
Materials and methods: Seventeen healthy subjects ages 18-43 participated in this study. Prior to the exercise protocol, the order of the oral applicance (OA) or no oral appliance (no OA) condition was randomly assigned to subjects, with subjects completing both conditions. Respiratory parameters (respiratory rate, ventilation, oxygen, and carbon dioxide) were measured between conditions while subjects ran for 10 min at steady state.
Results: The results demonstrated that both respiratory rate (25.97 BPM, OA and 28.35 BPM, no OA) and ventilation (47.66 l/min, OA and 50.34 l/min, No OA) were significantly lowered (p < .01) in the OA condition. There were no differences in carbon dioxide (1.89 l/min, no OA and 1.88 l/min, OA) or oxygen outcomes (2.17 l/min, no OA and 2.17 l/min OA).
Discussion: The outcomes from this study suggest that the design of the oral appliance elicits an effect on the genioglossus, thereby resulting in lowered respiratory rate and ventilation with no negative effects on oxygen uptake during exercise.
Keywords: exercise; genioglossus; oral appliance; respiratory rate; ventilation.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Arent, S. M. , McKenna, J. , & Golem, D. L. (2010). Effects of neuromuscular dentistry‐desgined mouthguard on muscular endurance and anaerobic power. Journal of Comparative Physiology, 7(2), 73–79.
-
- Bailey, S. P. , Willauer, T. J. , Balilionis, G. , Wilson, L. E. , Salley, J. T. , Bailey, E. K. , & Strickland, T. L. (2015). Effects of an over‐the‐counter vented mouthguard on cardiorespiratory responses to exercise and physical agility. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 29(3), 678–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

