Antibiotic Prescribing Choices and Their Comparative C. Difficile Infection Risks: A Longitudinal Case-Cohort Study
- PMID: 32069358
- PMCID: PMC7935390
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa124
Antibiotic Prescribing Choices and Their Comparative C. Difficile Infection Risks: A Longitudinal Case-Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Antibiotic use is the strongest modifiable risk factor for the development of Clostridioides difficile infection, but prescribers lack quantitative information on comparative risks of specific antibiotic courses. Our objective was to estimate risks of C. difficile infection associated with receipt of specific antibiotic courses.
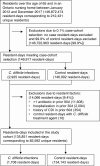
Methods: We conducted a longitudinal case-cohort analysis representing over 90% of Ontario nursing home residents, between 2012 and 2017. Our primary exposure was days of antibiotic receipt in the prior 90 days. Adjustment covariates included: age, sex, prior emergency department or acute care stay, Charlson comorbidity index, prior C. difficile infection, acid suppressant use, device use, and functional status. We examined incident C. difficile infection, including cases identified within the nursing home, and those identified during subsequent hospital admissions. Adjusted and unadjusted regression models were used to measure risk associated with 5- to 14-day courses of 18 different antibiotics.
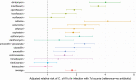
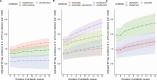
Results: We identified 1708 cases of C. difficile infection (1.27 per 100 000 resident-days). Longer antibiotic duration was associated with increased risk: 10- and 14-day courses incurred 12% (adjusted relative risk [ARR] = 1.12, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.09, 1.14) and 27% (ARR = 1.27, 95% CI: 1.21,1.30) more risk compared to 7-day courses. Among 7-day courses with similar indications: moxifloxacin resulted in 121% more risk than amoxicillin (ARR = 2.21, 95% CI: 1.67, 3.08), ciprofloxacin engendered 89% more risk than nitrofurantoin (ARR = 1.89, 95% CI: 1.45, 2.68), and clindamycin resulted in 112% (ARR = 2.12, 95% CI: 1.32, 3.78) more risk than cloxacillin.
Conclusions: C. difficile infection risk increases with antibiotic duration, and there are wide disparities in risks associated with antibiotic courses used for similar indications.
Keywords: Clostridioides difficile infection; CDI; antibiotics; cohort study; comparative effectiveness.
Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, as represented by the Public Health Ontario, 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Stevens V, Dumyati G, Fine LS, Fisher SG, van Wijngaarden E. Cumulative antibiotic exposures over time and the risk of Clostridium difficile infection. Clin Infect Dis 2011; 53:42–8. - PubMed
-
- Brown KA, Jones M, Daneman N, et al. Importation, antibiotics, and Clostridium difficile infection in veteran long-term care: a multilevel case-control study. Ann Intern Med 2016; 164:787–94. - PubMed
-
- Kavanagh K, Pan J, Marwick C, et al. Cumulative and temporal associations between antimicrobial prescribing and community-associated Clostridium difficile infection: population-based case-control study using administrative data. J Antimicrob Chemother 2017; 72:1193–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

