Dynamic Behavior of p53 Driven by Delay and a Microrna-34a-Mediated Feedback Loop
- PMID: 32070036
- PMCID: PMC7072921
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21041271
Dynamic Behavior of p53 Driven by Delay and a Microrna-34a-Mediated Feedback Loop
Abstract
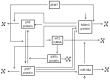
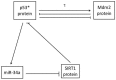
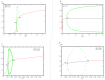
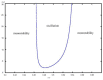
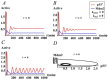
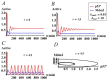
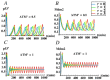
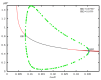
The tumor suppressor protein p53 is a critical hub in the comprehensive transcriptional network that inhibits the growth of cells after acute stress stimulation. In this paper, an integrated model of the p53 signaling pathway in response to DNA damage is proposed and the p53 stability and oscillatory dynamics are analyzed. Through theoretical analysis and numerical simulation, we find that the delay as a bifurcation parameter can drive the p53-Mdm2 module to undergo a supercritical Hopf bifurcation, thereby producing oscillation behavior. Moreover, we demonstrate how the positive feedback loop formed by p53* and microRNA-34a (miR-34a) with the feature of double-negative regulation produces limit-cycle oscillations. Further, we find that miR-34a can affect the critical value of Hopf bifurcation in delay-induced p53 networks. In addition, we show that ATM, once activated by DNA damage, makes p53* undergo two Hopf bifurcations. These results revealed that both time delay and miR-34a can have tumor suppressing roles by promoting p53 oscillation or high level expression, which will provide a perspective for promoting the development of anti-cancer drugs by targeting miR-34a and time delay.
Keywords: feedback loops; miR-34a; p53-Mdm2 pathway; time delay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-192-Mediated Positive Feedback Loop Controls the Robustness of Stress-Induced p53 Oscillations in Breast Cancer Cells.PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Dec 7;11(12):e1004653. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004653. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 26642352 Free PMC article.
-
Oscillatory Dynamics of p53 Genetic Network Induced by Feedback Loops and Time Delays.IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2019 Oct;18(4):611-621. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2019.2924079. Epub 2019 Jun 20. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2019. PMID: 31226080
-
Involvement of miR-605 and miR-34a in the DNA damage response promotes apoptosis induction.Biophys J. 2014 Apr 15;106(8):1792-800. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.02.032. Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 24739178 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative mechanisms of miR-34a regulation in cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Oct 12;8(10):e3100. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.495. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 29022903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[miR-34s--a tumor suppression protein p53 highly related microRNA].Yi Chuan. 2010 May;32(5):423-30. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2010.00423. Yi Chuan. 2010. PMID: 20466628 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Towards verifiable cancer digital twins: tissue level modeling protocol for precision medicine.Front Physiol. 2024 Oct 23;15:1473125. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1473125. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39507514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: The DNA damage response.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 21;13:1055911. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1055911. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36479202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual roles of SIRT1 in the BAX switch through the P53 module: A mathematical modeling study.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Oct 2;19:5578-5588. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.09.033. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34849192 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

