Gene polymorphisms and expression levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 in lumbar disc disease: a meta-analysis and immunohistochemical study
- PMID: 32070384
- PMCID: PMC7027108
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-020-01588-8
Gene polymorphisms and expression levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 in lumbar disc disease: a meta-analysis and immunohistochemical study
Abstract
Background: To investigate the association between interleukin-6 (IL-6) (rs1800795, rs1800796, rs1800797, rs13306435, rs2069849) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) (rs1800871, rs1800896) gene polymorphisms, expression levels, and lumbar disc disease (LDD).
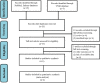
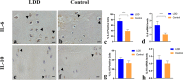
Methods: We conducted a literature research on PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) until February 28, 2019. We included all case-control studies about the association between IL-6 and IL-10 gene polymorphisms and LDD. The odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated to estimate the strength of association. Statistical analysis was conducted by Review Manager (RevMan) 5.3 software. Furthermore, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and RT-PCR were performed to evaluate IL-6 and IL-10 expressions in the normal and degenerated disc.
Results: A total of 6 studies, involving 1456 cases and 1611 controls, were included in this meta-analysis. G alleles of rs1800795 and rs1800797 in the IL-6 gene were significantly associated with LDD (rs1800795: G vs. C, OR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.16-1.64, P = 0.0002; rs1800797: G vs. A, OR = 1.35, 95% CI = 1.14-1.61, P = 0.0006). Begg's funnel plot and Egger's tests did not show any evidence of publication bias. IL-6 expression and IL-6 mRNA levels were significantly increased in the degenerated disc compared with those in the normal disc (IL-6 immunopositive cells, 73.68 ± 10.99% vs. 37.23 ± 6.42%, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: IL-6 gene polymorphisms (rs1800795 and rs1800797) were significantly associated with susceptibility to LDD. A high expression level of IL-6 may be an important risk factor for LDD.
Keywords: IL-10; IL-6; Lumbar disc disease; Meta-analysis; Polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gene locus polymorphisms and expression levels of interleukin-1 in lumbar disc disease: A MOOSE-compliant meta-analysis and immunohistochemical study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Oct 28;101(43):e31152. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031152. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36316862 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of the association between COL9A2 genetic polymorphisms and lumbar disc disease susceptibility.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014 Sep 15;39(20):1699-706. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000497. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014. PMID: 24983932
-
Vitamin D Receptor gene polymorphisms and plasma levels are associated with lumbar disc degeneration.Sci Rep. 2019 May 24;9(1):7829. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44373-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31127184 Free PMC article.
-
Association of IL-6, IL-10 and TGF-β1 gene polymorphisms with brucellosis: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Microb Pathog. 2019 Oct;135:103640. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103640. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31344477
-
Analysis of Interleukin-6 Gene Variants (rs1800795, rs1800796, rs1554606, rs1800797, rs2069840, rs12700386, and rs2069861) as Prognostic Markers in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Network Analysis.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2024 Jan;44(1):3-15. doi: 10.1089/jir.2023.0090. Epub 2023 Nov 29. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2024. PMID: 38029374
Cited by
-
Regulatory Effect of Inflammatory Mediators in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Apr 17;2023:6210885. doi: 10.1155/2023/6210885. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 37101594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A study of the association between polymorphisms in the genes for interleukins IL-6 and IL-10 and negative symptoms subdomains in schizophrenia.Indian J Psychiatry. 2022 Sep-Oct;64(5):484-488. doi: 10.4103/indianjpsychiatry.indianjpsychiatry_212_22. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Indian J Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36458089 Free PMC article.
-
Association between polymorphisms of collagen genes and susceptibility to intervertebral disc degeneration: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Oct 18;16(1):616. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02724-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34663366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Predictors of Early-Onset Spinal Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Part One of Two.Cureus. 2021 May 22;13(5):e15182. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15182. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34178503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine Imbalance as a Biomarker of Intervertebral Disk Degeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 25;24(3):2360. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032360. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768679 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Patrick N, Emanski E, Knaub MA. Acute and chronic low back pain. Med Clin North Am. 2014;98:777–789. - PubMed
-
- Selkirk SM, Ruff R. Low back pain, radiculopathy. Handb Clin Neurol. 2016;136:1027–1033. - PubMed
-
- Yang S, Kim W, Choi KH, Yi YG. Influence of occupation on lumbar spine degeneration in men: the Korean national health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010-2013. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2016;89:1321–1328. - PubMed
-
- Zawilla NH, Darweesh H, Mansour N, Helal S, Taha FM, Awadallah M, El Shazly R. Matrix metalloproteinase-3, vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms, and occupational risk factors in lumbar disc degeneration. J Occup Rehabil. 2014;24:370–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

