Gut microbiota mediates intermittent-fasting alleviation of diabetes-induced cognitive impairment
- PMID: 32071312
- PMCID: PMC7029019
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-14676-4
Gut microbiota mediates intermittent-fasting alleviation of diabetes-induced cognitive impairment
Abstract
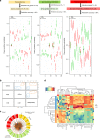
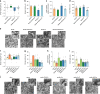
Cognitive decline is one of the complications of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Intermittent fasting (IF) is a promising dietary intervention for alleviating T2D symptoms, but its protective effect on diabetes-driven cognitive dysfunction remains elusive. Here, we find that a 28-day IF regimen for diabetic mice improves behavioral impairment via a microbiota-metabolites-brain axis: IF enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and energy metabolism gene expression in hippocampus, re-structures the gut microbiota, and improves microbial metabolites that are related to cognitive function. Moreover, strong connections are observed between IF affected genes, microbiota and metabolites, as assessed by integrative modelling. Removing gut microbiota with antibiotics partly abolishes the neuroprotective effects of IF. Administration of 3-indolepropionic acid, serotonin, short chain fatty acids or tauroursodeoxycholic acid shows a similar effect to IF in terms of improving cognitive function. Together, our study purports the microbiota-metabolites-brain axis as a mechanism that can enable therapeutic strategies against metabolism-implicated cognitive pathophysiologies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Atlas I. D. Brussels, Belgium: international diabetes federation; 2013. International Diabetes Federation (IDF), (2017).
-
- Gold S, et al. Hippocampal damage and memory impairments as possible early brain complications of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007;50:711–719. - PubMed
-
- De Felice FG, Ferreira STJD. Inflammation, defective insulin signaling, and mitochondrial dysfunction as common molecular denominators connecting type 2 diabetes to Alzheimer disease. Diabetes. 2014;63:2262–2272. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho C, Santos MS, Oliveira CR, Moreira PI. Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes-related alterations in brain mitochondria, autophagy and synaptic markers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2015;1852:1665–1675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

