Urinary tract infections: microbial pathogenesis, host-pathogen interactions and new treatment strategies
- PMID: 32071440
- PMCID: PMC7942789
- DOI: 10.1038/s41579-020-0324-0
Urinary tract infections: microbial pathogenesis, host-pathogen interactions and new treatment strategies
Abstract
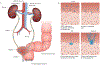
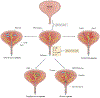
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common, recurrent infections that can be mild to life-threatening. The continued emergence of antibiotic resistance, together with our increasing understanding of the detrimental effects conferred by broad-spectrum antibiotic use on the health of the beneficial microbiota of the host, has underscored the weaknesses in our current treatment paradigm for UTIs. In this Review, we discuss how recent microbiological, structural, genetic and immunological studies have expanded our understanding of host-pathogen interactions during UTI pathogenesis. These basic scientific findings have the potential to shift the strategy for UTI treatment away from broad-spectrum antibiotics targeting conserved aspects of bacterial replication towards pathogen-specific antibiotic-sparing therapeutics that target core determinants of bacterial virulence at the host-pathogen interface.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests:
S.J.H. has an ownership interest in Fimbrion Therapeutics, and may benefit if the company is successful in marketing mannosides. S.J.H. is also the chief scientific officer of QureTech Bio. R.D.K. declares no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Foxman B, Barlow R, D’Arcy H, Gillespie B & Sobel JD Urinary tract infection: self-reported incidence and associated costs. Ann Epidemiol 10, 509–515 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Foxman B & Brown P Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: transmission and risk factors, incidence, and costs. Infect Dis Clin North Am 17, 227–241 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

