Morphometric Evaluation of the Seminiferous Tubules and the Antioxidant Protective Effects of Gallic Acid and Quercetin in the Testis and Liver of Butyl Phthalate Treated Rats
- PMID: 32071493
- PMCID: PMC6995466
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-018-0788-0
Morphometric Evaluation of the Seminiferous Tubules and the Antioxidant Protective Effects of Gallic Acid and Quercetin in the Testis and Liver of Butyl Phthalate Treated Rats
Abstract
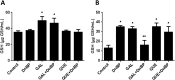
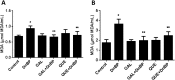
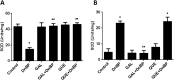
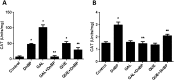
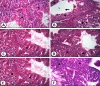
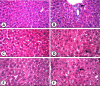
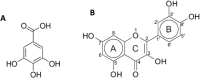
The antioxidant protective effects of gallic acid (GAL) and quercetin (QUE) against oxidative stress induced by di-butyl phthalate (DnBP) in the liver and testis of rats were evaluated in this study. Adult albino Wistar rats (180-225 g) were treated with QUE or GAL (50 mg/kg) alone or in combination with DnBP (1 mL/kg) for 15 days. After treatment, tissue samples were taken for determination of glutathione and malondialdehyde levels, and superoxide dismutase and catalase activities. Serial sections of the testis and liver were stained with haematoxylin and eosin for microscopy and seminiferous tubular morphometry. As expected, DnBP induced oxidative stress was evident by increased malondialdehyde level in both organs. Co-treatment with GAL or QUE reversed the malondialdehyde by 45.42, 37.44 and 37.57%, 23.32% and catalase by 52.21, 70.15 and 85%, 38.14% in the testis and liver respectively whereas superoxide dismutase activity and glutathione level were differently modulated parallel to histopathological improvement in both tissues. The seminiferous tubular diameter, epithelial height, epithelial germ cell count and tubular length were significantly decreased by 11.09, 51.91, 40.65 and 11.10% respectively versus control values after DnBP treatments and were attenuated on co-treatment with GAL or QUE. Co-treatment with GAL afforded better protective effects in both tissues but QUE treatment alone appeared more effective than GAL on the investigated morphometric data. It seems likely that GAL or QUE prevented the tissue damage but the antioxidant profiles of the liver and testis are different in response to the oxidative stress.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Di-n-butyl phthalate; Gallic acid; Morphometry; Oxidative stress; Quercetin.
© Association of Clinical Biochemists of India 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll authors of this manuscript are aware of this submission and declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
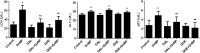
Similar articles
-
Effect of co-administration of gallic acid and quercetin or gallic acid and rutin on impaired spermatogenesis and oxidative damage in a busulfan-treated rat model.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2025 May;48(3):463-476. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2024.2369591. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 38948945
-
Evaluation of the protective effects of quercetin and gallic acid against oxidative toxicity in rat's kidney and HEK-293 cells.Toxicol Rep. 2020 Jul 31;7:955-962. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.07.015. eCollection 2020. Toxicol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32874919 Free PMC article.
-
Gallic acid ameliorates busulfan-induced testicular toxicity and damage in mature rats.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2022 Jul;45(4):1881-1890. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2021.1892949. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 33730944
-
Combined administration of curcumin and gallic acid inhibits gallic acid-induced suppression of steroidogenesis, sperm output, antioxidant defenses and inflammatory responsive genes.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Sep;143:49-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.02.008. Epub 2014 Feb 22. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24565563
-
Curcumin protects against gallic acid-induced oxidative stress, suppression of glutathione antioxidant defenses, hepatic and renal damage in rats.Ren Fail. 2016;38(2):321-9. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2015.1127743. Epub 2015 Dec 27. Ren Fail. 2016. PMID: 26707166
Cited by
-
Protective effect of quercetin against phthalates induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2022 Sep 16;11(5):863-871. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfac060. eCollection 2022 Oct. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2022. PMID: 36337248 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Abates Aluminum Trioxide Nanoparticles and Lead Acetate Induced Altered Sperm Quality, Testicular Oxidative Damage, and Sexual Hormones Disruption in Male Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 28;11(11):2133. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112133. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358505 Free PMC article.
-
Severe deterioration in sperm parameters and testes of rats administered naproxen and diclofenac at pre-puberty: An experimental study.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2022 Nov 2;20(10):831-840. doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v20i10.12267. eCollection 2022 Oct. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2022. PMID: 36381351 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Roles of Red Carrot Methanolic Extract and Vitamin E to Abrogate Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Challenge and Apoptosis in Rat Testes: Involvement of the Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 21;10(11):1653. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111653. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829524 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanisms mediating the inhibitory effects of quercetin against phthalates-induced testicular oxidative damage in rats].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Apr 20;43(4):577-584. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.04.10. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37202193 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Farombi EO, Abarikwu SO, Adedara IA, Oyeyemi MO. Kolaviron and curcumin ameliorate di-n-butylphthalate-induced testicular toxicity in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;100:43–48. - PubMed
-
- Abd-Ellah MF, Aly HAA, Mokhlis HAM, Abdel-Aziz AH. Quercetin attenuates di-(2 ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced testicular toxicity in adult rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2016;35:232–243. - PubMed
-
- Abarikwu SO, Pant AB, Farombi EO. Quercetin decreases steroidogenic enzyme activity, NF-κB expression and oxidative stress in cultured Leydig cells exposed to atrazine. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;373:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Kuppan G, Balasubramanyam J, Monickaraj F, Srinivasan G, Mohan V, Balasubramanyam M. Transcriptional regulation of cytokines and oxidative stress by gallic acid in human THP-1 monocytes. Cytokine. 2010;49:229–234. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
