Noninvasive stereotactic radioablation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation: First-in-man experience
- PMID: 32071622
- PMCID: PMC7011819
- DOI: 10.1002/joa3.12283
Noninvasive stereotactic radioablation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation: First-in-man experience
Abstract
Purpose: Catheter ablation is an effective therapy for atrial fibrillation (AF). However, risks remain, and improved efficacy is desired. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is a well-established therapy used to noninvasively treat malignancies and functional disorders with precision. We evaluated the feasibility of stereotactic radioablation for treating paroxysmal AF.
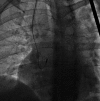
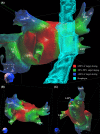
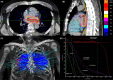
Methods: Two patients with drug-refractory paroxysmal AF underwent pulmonary vein isolation with SBRT. After placement of a percutaneous active fixation temporary pacing lead tracking fiducial, computed tomography (CT) angiography was performed to define left atrial anatomy. A tailored planning treatment volume was created to deliver contiguous linear ablations to isolate the pulmonary veins and posterior wall. Patients were treated on an outpatient basis in the radioablation suite. Clinical follow-up was performed through at least 24 months after therapy.
Results: Both patients successfully underwent SBRT planning and treatment without significant early or long-term side effects up to 48 months of follow-up. One patient had AF recurrence after 6 months free of arrhythmia, while the second patient remains free of AF after 24 months with fibrosis detected on MRI scan consistent with the ablation lesion set. An incidentally noted small pericardial effusion occurred in one patient.
Conclusion: Stereotactic radioablation may be feasible for the treatment of drug-refractory AF. Further evaluation is warranted.
Keywords: ablation; atrial fibrillation; new technology; noninvasive ablation; radioablation; stereotactic.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Arrhythmia published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of the Japanese Heart Rhythm Society.
Conflict of interest statement
PCZ: research support, consulting (Cyberheart); DW, EG, PM, AJ: employees (Cyberheart); TF: equity interest (Cyberheart); Others: none to report.
Figures

References
-
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B,, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur J Cardiothoracic Surg. 2016;50:e1–88. - PubMed
-
- Leksell L. The stereotaxic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand. 1951;102:316–9. - PubMed
-
- Videtic GMM, Hu C, Singh AK, Chang JY, Parker W, Olivier KR, et al. A randomized phase 2 study comparing 2 stereotactic body radiation therapy schedules for medically inoperable patients with stage I peripheral non‐small cell lung cancer: NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015;93:757–64. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haasbeek CJ, Lagerwaard FJ, Slotman BJ, Senan S. Outcomes of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for centrally located early‐stage lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:2036–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

