Nonunion - consensus from the 4th annual meeting of the Danish Orthopaedic Trauma Society
- PMID: 32071773
- PMCID: PMC7017598
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190037
Nonunion - consensus from the 4th annual meeting of the Danish Orthopaedic Trauma Society
Abstract
Nonunions are a relevant economic burden affecting about 1.9% of all fractures. Rather than specifying a certain time frame, a nonunion is better defined as a fracture that will not heal without further intervention.Successful fracture healing depends on local biology, biomechanics and a variety of systemic factors. All components can principally be decisive and determine the classification of atrophic, oligotrophic or hypertrophic nonunions. Treatment prioritizes mechanics before biology.The degree of motion between fracture parts is the key for healing and is described by strain theory. If the change of length at a given load is > 10%, fibrous tissue and not bone is formed. Therefore, simple fractures require absolute and complex fractures relative stability.The main characteristics of a nonunion are pain while weight bearing, and persistent fracture lines on X-ray.Treatment concepts such as 'mechanobiology' or the 'diamond concept' determine the applied osteosynthesis considering soft tissue, local biology and stability. Fine wire circular external fixation is considered the only form of true biologic fixation due to its ability to eliminate parasitic motions while maintaining load-dependent axial stiffness. Nailing provides intramedullary stability and biology via reaming. Plates are successful when complex fractures turn into simple nonunions demanding absolute stability. Despite available alternatives, autograft is the gold standard for providing osteoinductive and osteoconductive stimuli.The infected nonunion remains a challenge. Bacteria, especially staphylococcus species, have developed mechanisms to survive such as biofilm formation, inactive forms and internalization. Therefore, radical debridement and specific antibiotics are necessary prior to reconstruction. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2020;5:46-57. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190037.
Keywords: educative; fracture treatment; nonunion; principals; review; strain theory.
© 2020 The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of interest statement: HS reports payments from Arthrex for lectures and European research grants from HIPGEN Horizon 2020 and Bonebank Interreg 5 outside the submitted work. MBr reports employment as Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon at Odense University Hospital and as Associate Professor at the University; and receipt of royalties as the author of textbooks on basic orthopaedics outside the submitted work. NF reports consultancy for Orthofix SRL; employment at Tygerberg Hospital, Western Cape Department of Health; and payment for lectures as a trauma and limb reconstruction course presenter for Smith & Nephew, all outside the submitted work. AT reports being a paid faculty member at the Masters Fracture Forum Huntington Beach California, April 2019, with expenses and honorarium received, outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflict of interest relevant to this work.
Figures




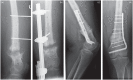
References
-
- Miramini S, Zhang L, Richardson M, Mendis P, Oloyede A, Ebeling P. The relationship between interfragmentary movement and cell differentiation in early fracture healing under locking plate fixation. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 2016;39:123–133. - PubMed
-
- Zimmermann G, Henle P, Küsswetter M, et al. TGF-beta1 as a marker of delayed fracture healing. Bone 2005;36:779–785. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

