Genome-wide identification and characterization of the soybean SOD family during alkaline stress
- PMID: 32071807
- PMCID: PMC7007734
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.8457
Genome-wide identification and characterization of the soybean SOD family during alkaline stress
Abstract
Background: Superoxide dismutase (SOD) proteins, as one kind of the antioxidant enzymes, play critical roles in plant response to various environment stresses. Even though its functions in the oxidative stress were very well characterized, the roles of SOD family genes in regulating alkaline stress response are not fully reported.
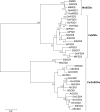
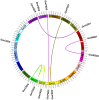
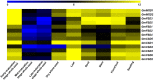
Methods: We identified the potential family members by using Hidden Markov model and soybean genome database. The neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree and exon-intron structures were generated by using software MEGA 5.0 and GSDS online server, respectively. Furthermore, the conserved motifs were analyzed by MEME online server. The syntenic analysis was conducted using Circos-0.69. Additionally, the expression levels of soybean SOD genes under alkaline stress were identified by qRT-PCR.
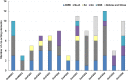
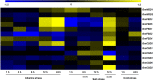
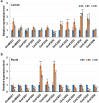
Results: In this study, we identified 13 potential SOD genes in soybean genome. Phylogenetic analysis suggested that SOD genes could be classified into three subfamilies, including MnSODs (GmMSD1-2), FeSODs (GmFSD1-5) and Cu/ZnSODs (GmCSD1-6). We further investigated the gene structure, chromosomal locations and gene-duplication, conserved domains and promoter cis-elements of the soybean SOD genes. We also explored the expression profiles of soybean SOD genes in different tissues and alkaline, salt and cold stresses, based on the transcriptome data. In addition, we detected their expression patterns in roots and leaves by qRT-PCR under alkaline stress, and found that different SOD subfamily genes may play different roles in response to alkaline stress. These results also confirmed the hypothesis that the great evolutionary divergence may contribute to the potential functional diversity in soybean SOD genes. Taken together, we established a foundation for further functional characterization of soybean SOD genes in response to alkaline stress in the future.
Keywords: Alkaline; Evolution; Expression patterns; Phylogenetic analysis; Soybean.
© 2020 Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Artimo P, Jonnalagedda M, Arnold K, Baratin D, Csardi G, De Castro E, Duvaud S, Flegel V, Fortier A, Gasteiger E, Grosdidier A, Hernandez C, Ioannidis V, Kuznetsov D, Liechti R, Moretti S, Mostaguir K, Redaschi N, Rossier G, Xenarios I, Stockinger H. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Research. 2012;40(W1):W597–W603. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks400. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

