2019 Novel coronavirus: where we are and what we know
- PMID: 32072569
- PMCID: PMC7095345
- DOI: 10.1007/s15010-020-01401-y
2019 Novel coronavirus: where we are and what we know
Erratum in
-
Correction to: 2019 Novel coronavirus: where we are and what we know.Infection. 2021 Feb;49(1):197. doi: 10.1007/s15010-020-01552-y. Infection. 2021. PMID: 33210242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correction: 2019 Novel coronavirus: where we are and what we know.Infection. 2022 Dec;50(6):1637. doi: 10.1007/s15010-022-01894-9. Infection. 2022. PMID: 36030335 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correction: 2019 Novel coronavirus: where we are and what we know.Infection. 2023 Jun;51(3):801. doi: 10.1007/s15010-023-01991-3. Infection. 2023. PMID: 36867311 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
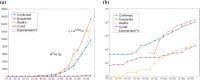
There is a current worldwide outbreak of a new type of coronavirus (2019-nCoV), which originated from Wuhan in China and has now spread to 17 other countries. Governments are under increased pressure to stop the outbreak spiraling into a global health emergency. At this stage, preparedness, transparency, and sharing of information are crucial to risk assessments and beginning outbreak control activities. This information should include reports from outbreak sites and from laboratories supporting the investigation. This paper aggregates and consolidates the virology, epidemiology, clinical management strategies from both English and Chinese literature, official news channels, and other official government documents. In addition, by fitting the number of infections with a single-term exponential model, we report that the infection is spreading at an exponential rate, with a doubling period of 1.8 days.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; COVID-19; China; Clinical guideline; Coronavirus; Epidemiology; Literature review; Literature survey; Novel coronavirus; Review; Virology; Wuhan.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guo Q, Li M, Wang C, Wang P, Fang Z, Tan J, et al. Host and infectivity prediction of Wuhan 2019 novel coronavirus using deep learning algorithm. bioRxiv. 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources