Effect of 6% hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 on kidney and haemostatic function in cardiac surgical patients: a randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 32072617
- PMCID: PMC9291605
- DOI: 10.1111/anae.14994
Effect of 6% hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 on kidney and haemostatic function in cardiac surgical patients: a randomised controlled trial
Abstract
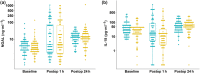
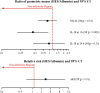
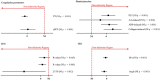
Whether third-generation hydroxyethyl starch solutions provoke kidney injury or haemostatic abnormalities in patients having cardiac surgery remains unclear. We tested the hypotheses that intra-operative administration of a third-generation starch does not worsen postoperative kidney function or haemostasis in cardiac surgical patients compared with human albumin 5%. This triple-blind, non-inferiority, clinical trial randomly allocated patients aged 40-85 who underwent elective aortic valve replacement, with or without coronary artery bypass grafting, to plasma volume replacement with 6% starch 130/0.4 vs. 5% human albumin. Our primary outcome was postoperative urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations, a sensitive and early marker of postoperative kidney injury. Secondarily, we evaluated urinary interleukin-18; acute kidney injury using creatinine RIFLE criteria, coagulation measures, platelet count and function. Non-inferiority (delta 15%) was assessed with correction for multiple comparisons. We enrolled 141 patients (69 starch, 72 albumin) as planned. Results of the primary analysis demonstrated that postoperative urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (median (IQR [range])) was slightly lower with hydroxyethyl starch (5 (1-68 [0-996]) ng.ml-1 ) vs. albumin (5 (2-74 [0-1604]) ng.ml-1 ), although not non-inferior [ratio of geometric means (95%CI) 0.91 (0.57, 1.44); p = 0.15] due to higher than expected variability. Urine interleukin-18 concentrations were reduced, but interleukin-18 and kidney injury were again not non-inferior. Of 11 individual coagulation measures, platelet count and function, nine were non-inferior to albumin. Two remaining measures, thromboelastographic R value and arachidonic acid-induced platelet aggregation, were clinically similar but with wide confidence intervals. Starch administration during cardiac surgery produced similar observed effects on postoperative kidney function, coagulation, platelet count and platelet function compared with albumin, though greater than expected variability and wide confidence intervals precluded the conclusion of non-inferiority. Long-term mortality and kidney function appeared similar between starch and albumin.
3세대 하이드록시에틸 전분 용액이 심장수술을 받는 환자 에게 신장손상이나 혈액응고 장애를 유발하는지는 여전히 불 분명하다. 이에 본 연구에서는 심장수술 중 3세대 전분을 투 여해도, 수술 후 신장 기능이나 지혈이 5% 사람혈청알부민 투 여와 비교하였을 때 악화되지 않는다는 가설을 검정하였다. 이 삼중맹검 비열등성 임상 연구는 관상동맥우회술이 동반 또는 동반되지 않는 대동맥 판막 치환술을 시행받는 40‐85세 의 환자에서 혈장 보충을 의하여 5% 사람혈청알부민 혹은 6% 녹말 130/0.4%을 무작위로 사용하였다. 저자들의 일차 연 구 결과는 수술 후 신장 손상의 민감한 초기 표식인자로 알려 져 있는 소변 중성 젤라틴 효소 관련 리포칼린(urinary neu‐ trophil gelatinase‐associated lipocalin, NGAL) 농도이다. 이차 연구 결과들로는 소변 인터루킨‐18, RIFLE 기준 급성 신 손상, 혈액응고 지표, 혈소판 수 및 기능을 평가하였다. 비열 등성(델타 15%)은 다중 비교를 위해 보정하고 평가되었다. 저 자들은 141명의 환자(69 전분, 72 알부민)를 계획대로 등록하 였다. 일차 연구 결과는 수술 후 소변 NGAL (중위수 (사분위 ‐ 수범위[범위])이 알부민(5 (2–74 [0–1604]) ng.ml‐1) 대비 하이 드록시에틸 전분(5 (1–68 [0–996] ng.ml‐1)에서 약간 낮았지만 예상보다 높은 변동성으로 인해 비열등함을 보였다[기하학적 평균의 비율(95% 신뢰구간) 0.91 (0.57, 1.44); p = 0.15]. 소변 인터루킨‐18 농도는 감소하였지만 인터루킨‐18과 신장손상 또한 비열등함을 보였다. 열한 가지의 개별 응고 검사들과 혈 소판 수 및 기능 검사 중에서 9개는 알부민보다 비열등함을 보였다. 나머지 두 가지 측정치인 혈전탄성묘사도 R값과 아라 키돈산‐유도 혈소판 응집은 임상적으로 유사하였지만 신뢰구 간이 넓었다. 심장수술 중 녹말 투여는 알부민에 비해 수술 후 신장기능, 혈액응고, 혈소판 수 및 기능에 대해 유사한 효과를 나타냈지만, 측정치들의 예상보다 큰 변동성과 넓은 신뢰구간 으로 인하여 명확한 비열등성을 결론지을 수는 없었다. 장기 간 사망률과 신장 기능은 녹말과 알부민 군에서 모두 유사하 였다.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02192502.
Keywords: cardiac surgery; hydroxyethyl starch; urinary interleukin-18; urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin.
© 2020 The Authors. Anaesthesia published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association of Anaesthetists.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hydroxyethyl starch on kidney and haemostatic function in cardiac surgical patients: is a non-inferiority study design appropriate for this setting?Anaesthesia. 2021 Apr;76(4):576. doi: 10.1111/anae.15386. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Anaesthesia. 2021. PMID: 33464559 No abstract available.
References
-
- Myburgh JA, Finfer S, Bellomo R, et al. Hydroxyethyl starch or saline for fluid resuscitation in intensive care. New England Journal of Medicine 2012; 367: 1901–11. - PubMed
-
- Perner A, Haase N, Guttormsen AB, et al. Hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.42 versus Ringer's acetate in severe sepsis. New England Journal of Medicine 2012; 367: 124–34. - PubMed
-
- Kabon B, Sessler DI, Kurz A, et al. Effect of intraoperative goal‐directed balanced crystalloid versus colloid administration on major postoperative morbidity: a randomized trial. Anesthesiology 2019; 130: 728–44. - PubMed
-
- Joosten A, Delaporte A, Ickx B, et al. Crystalloid versus colloid for intraoperative goal‐directed fluid therapy using a closed‐loop system: a randomized, double‐blinded, controlled trial in major abdominal surgery. Anesthesiology 2018; 128: 55–66. - PubMed
-
- Joosten A, Delaporte A, Mortier J, et al. Long‐term impact of crystalloid versus colloid solutions on renal function and disability‐free survival after major abdominal surgery. Anesthesiology 2019; 130: 227–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

