Fracture Toughness Analysis of Epoxy-Recycled Rubber-Based Composite Reinforced with Graphene Nanoplatelets for Structural Applications in Automotive and Aeronautics
- PMID: 32074973
- PMCID: PMC7077629
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12020448
Fracture Toughness Analysis of Epoxy-Recycled Rubber-Based Composite Reinforced with Graphene Nanoplatelets for Structural Applications in Automotive and Aeronautics
Abstract
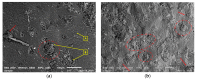
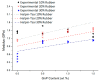
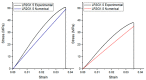
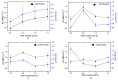
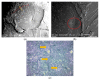
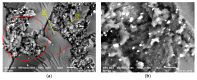
This study proposes a new design of lightweight and cost-efficient composite materials for the aeronautic industry utilizing recycled fresh scrap rubber, epoxy resin, and graphene nanoplatelets (GnPs). After manufacturing the composites, their bending strength and fracture characteristics were investigated by three-point bending (3PB) tests. Halpin-Tsai homogenization adapted to composites containing GnPs was used to estimate the moduli of the composites, and satisfactory agreement with the 3PB test results was observed. In addition, 3PB tests were simulated by finite element method incorporating the Halpin-Tsai homogenization, and the resulting stress-strain curves were compared with the experimental results. Mechanical test results showed that the reinforcement with GnPs generally increased the modulus of elasticity as well as the fracture toughness of these novel composites. Toughening mechanisms were evaluated by SEM fractography. The typical toughening mechanisms observed were crack deflection and cavity formation. Considering the advantageous effects of GnPs on these novel composites and cost efficiency gained by the use of recycled rubber, these composites have the potential to be used to manufacture various components in the automotive and aeronautic industries as well as smart building materials in civil engineering applications.
Keywords: Halpin–Tsai; SEM; graphene nanoplatelets; recycled rubber; toughening mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- May C. Epoxy Resins: Chemistry and Technology. 2nd ed. CRC Press; London, UK: 1987. pp. 46–121.
-
- Johnsen B.B., Kinloch A.J., Mohammed R.D., Taylor A.C., Sprenger S. Toughening mechanisms of nanoparticle-modified epoxy polymers. Polymer. 2007;48:530–541. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2006.11.038. - DOI
-
- Liang Y.L., Pearson R.A. The toughening mechanism in hybrid epoxy-silica-rubber nanocomposites (HESRNs) Polymer. 2010;51:4880–4890. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2010.08.052. - DOI
-
- Irez A.B., Miskioglu I., Bayraktar E. Toughening Mechanisms on Recycled Rubber Modified Epoxy Based Composites Reinforced with Graphene Nanoplatelets. In: Thakre P.R., Singh P.R., Slipher G., editors. Mechanics of Composite, Hybrid and Multifunctional Materials. 1st ed. Volume 5. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2019. pp. 283–290. - DOI
-
- Adhikari B., De D., Maiti S. Reclamation and recycling of waste rubber. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000;25:909–948. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6700(00)00020-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

