Microfluidics in Haemostasis: A Review
- PMID: 32075008
- PMCID: PMC7070452
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25040833
Microfluidics in Haemostasis: A Review
Abstract
Haemostatic disorders are both complex and costly in relation to both their treatment and subsequent management. As leading causes of mortality worldwide, there is an ever-increasing drive to improve the diagnosis and prevention of haemostatic disorders. The field of microfluidic and Lab on a Chip (LOC) technologies is rapidly advancing and the important role of miniaturised diagnostics is becoming more evident in the healthcare system, with particular importance in near patient testing (NPT) and point of care (POC) settings. Microfluidic technologies present innovative solutions to diagnostic and clinical challenges which have the knock-on effect of improving health care and quality of life. In this review, both advanced microfluidic devices (R&D) and commercially available devices for the diagnosis and monitoring of haemostasis-related disorders and antithrombotic therapies, respectively, are discussed. Innovative design specifications, fabrication techniques, and modes of detection in addition to the materials used in developing micro-channels are reviewed in the context of application to the field of haemostasis.
Keywords: Coagulation; LOC; MEMS; POC; haemostasis; microfluidics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
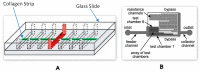

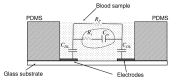


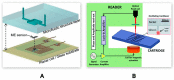
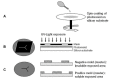


References
-
- Convery N., Gadegaard N. 30 Years of Microfluidics. Micro Nano Eng. 2019;2:76–91. doi: 10.1016/j.mne.2019.01.003. - DOI
-
- Chiu D.T., de Mello A.J., Di Carlo D., Doyle P.S., Hansen C., Maceiczyk R.M., Wootton R.C.R. Small but Perfectly Formed? Successes, Challenges, and Opportunities for Microfluidics in the Chemical and Biological Sciences. Chem. 2017;2:201–223. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2017.01.009. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

