Detection of the Ovarian Cancer Biomarker Lysophosphatidic Acid in Serum
- PMID: 32075013
- PMCID: PMC7168251
- DOI: 10.3390/bios10020013
Detection of the Ovarian Cancer Biomarker Lysophosphatidic Acid in Serum
Abstract
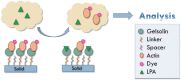
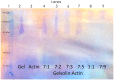
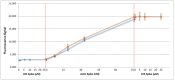
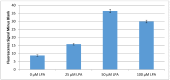
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is present during the medical condition of ovarian cancer at all stages of the disease, and, therefore possesses considerable potential as a biomarker for screening its presence in female patients. Unfortunately, there is currently no clinically employable assay for this biomarker. In the present work, we introduce a test based on the duel protein system of actin and gelsolin that could allow the quantitative measurement of LPA in serum samples in a biosensing format. In order to evaluate this possibility, actin protein was dye-modified and complexed with gelsolin protein, followed by surface deposition onto silica nanoparticles. This solid-phase system was exposed to serum samples containing various concentrations of LPA and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Measurements conducted for the LPA-containing serum samples were higher after exposure to the developed test than samples without LPA. Early results suggest a limit of detection of 5 μM LPA in serum. The eventual goal is to employ the chemistry described here in a biosensor configuration for the large population-scale, rapid screening of women for the potential occurrence of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: actin; fluorescence detection; gelsolin; lysophosphatidic acid; ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- De La Franier B., Thompson M. Biosensors and Methods for Detection of Lysophosphatidic Acid for Signaling of Ovarian Cancer. US 15/572,295. U.S. Pantent. 2018 May 31;
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

