Dickkopf-2 (DKK2) as Context Dependent Factor in Patients with Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 32075129
- PMCID: PMC7072714
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12020451
Dickkopf-2 (DKK2) as Context Dependent Factor in Patients with Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
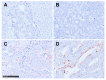
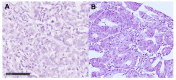
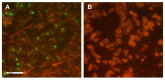
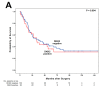
Dickkopf-2 (DKK2) has been described as Wnt/beta-catenin pathway antagonist and its expression is mediated by micro RNA-221 (miRNA-221). So far, there is only limited data characterizing the role of DKK2 expression in esophageal cancer. A tissue micro array of 192 patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma was analyzed immunohistochemically for DKK2, miRNA-221 expression by RNA scope, and GATA6 amplification by fluorescence in-situ hybridization. The data was correlated with clinical, pathological and molecular data (TP53, HER2, c-myc, GATA6, PIK3CA, and KRAS amplifications). DKK2 expression was detectable in 21.7% and miRNA-221 expression in 33.5% of the patients. We observed no correlation between DKK2 or miRNA-221 expression and clinico-pathological data DKK2 expression was correlated with TP53 mutations and amplification of GATA6. We did not detect a survival difference in dependence of DKK2 for the total cohort, however, in patients without neoadjuvant treatment DKK2 expression correlated with a prolonged survival (median overall-survival 202 vs. 55 months, p = 0.012) which turned opposite in patients that underwent neoadjuvant treatment. High amounts of miRNA-221 were in trend associated with a prolonged overall-survival (p = 0.070). DKK2 as a Wnt antagonist is associated with prolonged survival in patients without neoadjuvant treatment and changes its prognostic value to the contrary in patients after neoadjuvant therapy. The modulatory effects of neoadjuvant treatment in connection with DKK2 expression are not fully understood, but when considering DKK2 as a tumor marker, it is necessary to see it in the context of neoadjuvant therapy.
Keywords: DKK2; EAC; GATA6; response prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shapiro J., Van Lanschot J.J.B., Hulshof M., Van Hagen P., Van Berge Henegouwen M.I., Wijnhoven B.P.L., Van Laarhoven H.W.M., Nieuwenhuijzen G.A.P., Hospers G.A.P., Bonenkamp J.J., et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for oesophageal or junctional cancer (cross): Long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1090–1098. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00040-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al-Batran S.E., Hofheinz R.D., Pauligk C., Kopp H.G., Haag G.M., Luley K.B., Meiler J., Homann N., Lorenzen S., Schmalenberg H., et al. Histopathological regression after neoadjuvant docetaxel, oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin versus epirubicin, cisplatin, and fluorouracil or capecitabine in patients with resectable gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (flot4-aio): Results from the phase 2 part of a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 2/3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:1697–1708. - PubMed
-
- Coccolini F., Nardi M., Montori G., Ceresoli M., Celotti A., Cascinu S., Fugazzola P., Tomasoni M., Glehen O., Catena F., et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced gastric and esophago-gastric cancer. Meta-analysis of randomized trials. Int. J. Surg. 2018;51:120–127. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.01.008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

