p53's Extended Reach: The Mutant p53 Secretome
- PMID: 32075247
- PMCID: PMC7072272
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10020307
p53's Extended Reach: The Mutant p53 Secretome
Abstract
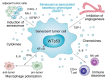
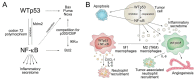
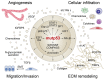
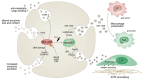
p53 suppresses tumorigenesis by activating a plethora of effector pathways. While most of these operate primarily inside of cells to limit proliferation and survival of incipient cancer cells, many extend to the extracellular space. In particular, p53 controls expression and secretion of numerous extracellular factors that are either soluble or contained within extracellular vesicles such as exosomes. As part of the cellular secretome, they execute key roles in cell-cell communication and extracellular matrix remodeling. Mutations in the p53-encoding TP53 gene are the most frequent genetic alterations in cancer cells, and therefore, have profound impact on the composition of the tumor cell secretome. In this review, we discuss how the loss or dominant-negative inhibition of wild-type p53 in concert with a gain of neomorphic properties observed for many mutant p53 proteins, shapes a tumor cell secretome that creates a supportive microenvironment at the primary tumor site and primes niches in distant organs for future metastatic colonization.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular vesicles; metastasis; p53; pre-metastatic niches; secretome; tumor microenvironment; tumor suppressor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Levine A.J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989;57:1083–1093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

