The Biological and Chemical Diversity of Tetramic Acid Compounds from Marine-Derived Microorganisms
- PMID: 32075282
- PMCID: PMC7074263
- DOI: 10.3390/md18020114
The Biological and Chemical Diversity of Tetramic Acid Compounds from Marine-Derived Microorganisms
Abstract
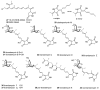
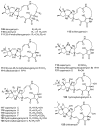
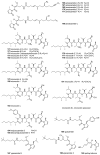
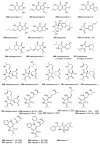
Tetramic acid (pyrrolidine-2,4-dione) compounds, isolated from a variety of marine and terrestrial organisms, have attracted considerable attention for their diverse, challenging structural complexity and promising bioactivities. In the past decade, marine-derived microorganisms have become great repositories of novel tetramic acids. Here, we discuss the biological activities of 277 tetramic acids of eight classifications (simple 3-acyl tetramic acids, 3-oligoenoyltetramic acids, 3-decalinoyltetramic acid, 3-spirotetramic acids, macrocyclic tetramic acids, N-acylated tetramic acids, α-cyclopiazonic acid-type tetramic acids, and other tetramic acids) from marine-derived microbes, including fungi, actinobacteria, bacteria, and cyanobacteria, as reported in 195 research studies up to 2019.
Keywords: bioactivity; marine natural product; marine-derived microorganisms; tetramic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
















References
-
- Royles B.J. Naturally occurring tetramic acids: Structure, isolation, and synthesis. Chem. Rev. 1995;95:1981–2001. doi: 10.1021/cr00038a009. - DOI
-
- Ghisalberti E.L. Studies in Natural Products Chemistry. Volume 28. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2003. Bioactive Tetramic Acid Metabolites; pp. 109–163.
-
- Gossauer A. Monopyrrolic natural compounds including tetramic acid derivatives. Chem. Org. Nat. 2003;86:1–188. - PubMed
-
- Mo X., Li Q., Ju J. Naturally occurring tetramic acid products: Isolation, structure elucidation and biological activity. RSC Adv. 2014;4:50566–50593. doi: 10.1039/C4RA09047K. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

