Cortico-Thalamo-Cortical Circuits of Mouse Forelimb S1 Are Organized Primarily as Recurrent Loops
- PMID: 32075900
- PMCID: PMC7117898
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2277-19.2020
Cortico-Thalamo-Cortical Circuits of Mouse Forelimb S1 Are Organized Primarily as Recurrent Loops
Abstract
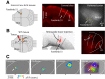
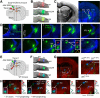
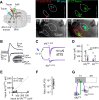
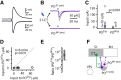
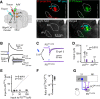
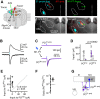
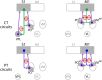
Cortical projections to the thalamus arise from corticothalamic (CT) neurons in layer 6 and pyramidal tract-type (PT) neurons in layer 5B. We dissected the excitatory synaptic connections in the somatosensory thalamus formed by CT and PT neurons of the primary somatosensory (S1) cortex, focusing on mouse forelimb S1. Mice of both sexes were studied. The CT neurons in S1 synaptically excited S1-projecting thalamocortical (TC) neurons in subregions of both the ventral posterior lateral and posterior (PO) nuclei, forming a pair of recurrent cortico-thalamo-cortical (C-T-C) loops. The PT neurons in S1 also formed a recurrent loop with S1-projecting TC neurons in the same subregion of the PO. The PT neurons in the adjacent primary motor (M1) cortex formed a separate recurrent loop with M1-projecting TC neurons in a nearby subregion of the PO. Collectively, our results reveal that C-T-C circuits of mouse forelimb S1 are primarily organized as multiple cortical cell-type-specific and thalamic subnucleus-specific recurrent loops, with both CT and PT neurons providing the strongest excitatory input to TC neurons that project back to S1. The findings, together with those of related studies of C-T-C circuits, thus suggest that recurrently projecting thalamocortical neurons are the principal targets of cortical excitatory input to the mouse somatosensory and motor thalamus.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Bidirectional cortical communication with the thalamus is considered an important aspect of sensorimotor integration for active touch in the somatosensory system, but the cellular organization of the circuits mediating this process is not well understood. We used an approach combining cell-type-specific anterograde optogenetic excitation with single-cell recordings targeted to retrogradely labeled thalamocortical neurons to dissect these circuits. The findings reveal a consistent pattern: cortical projections to the somatosensory thalamus target thalamocortical neurons that project back to the same cortical area. Commonalities of these findings to previous descriptions of related circuits in other areas suggest that cortico-thalamo-cortical circuits may generally be organized primarily as recurrent loops.
Keywords: channelrhodopsin; connectivity; corticothalamic; motor; somatosensory; thalamocortical.
Copyright © 2020 the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anterolateral Motor Cortex Connects with a Medial Subdivision of Ventromedial Thalamus through Cell Type-Specific Circuits, Forming an Excitatory Thalamo-Cortico-Thalamic Loop via Layer 1 Apical Tuft Dendrites of Layer 5B Pyramidal Tract Type Neurons.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 10;38(41):8787-8797. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1333-18.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 24. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30143573 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic circuit organization of motor corticothalamic neurons.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 4;35(5):2293-307. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4023-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25653383 Free PMC article.
-
An Ultrastructural Study of the Thalamic Input to Layer 4 of Primary Motor and Primary Somatosensory Cortex in the Mouse.J Neurosci. 2017 Mar 1;37(9):2435-2448. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2557-16.2017. Epub 2017 Jan 30. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28137974 Free PMC article.
-
Untangling the cortico-thalamo-cortical loop: cellular pieces of a knotty circuit puzzle.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021 Jul;22(7):389-406. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00459-3. Epub 2021 May 6. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33958775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spike timing and synaptic dynamics at the awake thalamocortical synapse.Prog Brain Res. 2005;149:91-105. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(05)49008-1. Prog Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 16226579 Review.
Cited by
-
A Closer Look at Corticothalamic "Loops".Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Feb 2;15:632668. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.632668. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 33603649 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Connectivity of single neurons classifies cell subtypes in mouse brains.Nat Methods. 2025 Apr;22(4):861-873. doi: 10.1038/s41592-025-02621-6. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Nat Methods. 2025. PMID: 40119176 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic properties of layer 6 auditory corticothalamic inputs in normal hearing and noise-induced hearing loss.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 11:2025.07.08.663770. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.08.663770. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40672338 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Corticothalamic Pathways From Layer 5: Emerging Roles in Computation and Pathology.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Sep 9;15:730211. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.730211. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 34566583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protocol for mouse optogenetic fMRI at ultrahigh magnetic fields.STAR Protoc. 2022 Dec 16;3(4):101846. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101846. Epub 2022 Dec 12. STAR Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36595930 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
