lncRNA-DNA hybrids regulate distant genes
- PMID: 32078233
- PMCID: PMC7054664
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.202050107
lncRNA-DNA hybrids regulate distant genes
Abstract
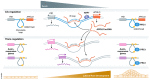
lncRNAs actively regulate gene expression. They contribute to chromosomal interactions at close or distant genomic regions, which, in turn, regulate transcription [1]. Ariel et al [2] reveal in a recent study a new molecular mechanism of the Arabidopsis lncRNA APOLO. The authors extend previously reported functions of APOLO in cis-regulation of chromosomal looping and transcription of its neighbor gene to a set of distant genes involved in auxin-induced molecular pathways controlling lateral root development. Noteworthy, APOLO recognition of multiple trans-modulated targets occurs through a novel mechanism involving R-loop formation.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures
Comment on
-
R-Loop Mediated trans Action of the APOLO Long Noncoding RNA.Mol Cell. 2020 Mar 5;77(5):1055-1065.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.12.015. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 31952990
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

