Novel Blood-Brain Barrier Shuttle Peptides Discovered through the Phage Display Method
- PMID: 32079185
- PMCID: PMC7070575
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25040874
Novel Blood-Brain Barrier Shuttle Peptides Discovered through the Phage Display Method
Abstract
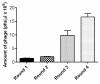
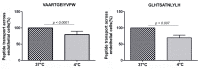
Delivery of therapeutic agents into the brain is a major challenge in central nervous system drug development. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) prevents access of biotherapeutics to their targets in the central nervous system and, therefore, prohibits the effective treatment of many neurological disorders. To find blood-brain barrier shuttle peptides that could target therapeutics to the brain, we applied a phage display technology on a primary endothelial rat cellular model. Two identified peptides from a 12 mer phage library, GLHTSATNLYLH and VAARTGEIYVPW, were selected and their permeability was validated using the in vitro BBB model. The permeability of peptides through the BBB was measured by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled to a triple-quadrupole mass spectrometer (UHPLC-MS/MS). We showed higher permeability for both peptides compared to N-C reversed-sequence peptides through in vitro BBB: for peptide GLHTSATNLYLH 3.3 × 10-7 cm/s and for peptide VAARTGEIYVPW 1.5 × 10-6 cm/s. The results indicate that the peptides identified by the in vitro phage display technology could serve as transporters for the administration of biopharmaceuticals into the brain. Our results also demonstrated the importance of proper BBB model for the discovery of shuttle peptides through phage display libraries.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier; phage display; shuttle peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

