Failure of Less-Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) plating for periprosthetic distal femur fractures: Three case reports
- PMID: 32080105
- PMCID: PMC7034731
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019195
Failure of Less-Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) plating for periprosthetic distal femur fractures: Three case reports
Abstract
Rationale: Less-Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) plate is an internal fixation commonly used for the periprosthetic distal femur fractures. Failure associated with LISS plate has been rarely reported, and the reasons for LISS plate failure are multitudinous. Various advantages have been reported, but failures continue.
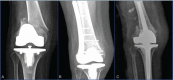
Patient concerns: We present 3 cases illustrating the failure of Less-Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) plating for periprosthetic distal femur fractures. The shaft screws of the LISS plate broke in 2 cases, and the plate placement was incorrect in 1 case. Early weight bearing, obesity, osteoporosis, and lateral collateral ligament injury due to incorrect plate placement constituted the etiologies of LISS plate failure.
Diagnosis: Failure of Less-Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) plating for periprosthetic distal femur fractures after Total knee arthroplasty.
Interventions: Three patients underwent Less-Invasive Stabilization System plates removal with replacement of the total knee arthroplasty revision surgery with rotating hinged knee prosthesis.
Outcomes: After completing the total knee arthroplasty revision surgery, all patients underwent regular follow-up examinations. Case 2 could walk unaided, without pain, final union was confirmed for both case 1 and case 3.
Conclusion: Less-Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) plate provides satisfactory results in periprosthetic fractures after Total knee arthroplasty (TKA). The LISS plate has many advantages, but failures continue to occur. The causes for failure were early weight bearing, obesity, osteoporosis, and lateral collateral ligament (LCL) injury due to incorrect plate placement in our series. We recommend that protection or properly delay of weight-bearing, active anti-osteoporosis treatment, and intraoperative fluoroscopy are the effective methods to avoid failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Osteosynthesis for periprosthetic supracondylar fracture above a total knee arthroplasty using a locking compression plate].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2009 Dec;76(6):473-8. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2009. PMID: 20067694 Czech.
-
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with dual plating for periprosthetic distal femoral fractures following total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Jul 6;16(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02586-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34229703 Free PMC article.
-
Early Mechanical Failures of the Synthes Variable Angle Locking Distal Femur Plate.J Orthop Trauma. 2016 Jan;30(1):e7-e11. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000391. J Orthop Trauma. 2016. PMID: 26849390
-
Equivalent union rates between intramedullary nail and locked plate fixation for distal femur periprosthetic fractures - a systematic review.Injury. 2020 Apr;51(4):1062-1068. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2020.02.043. Epub 2020 Feb 16. Injury. 2020. PMID: 32115204
-
Similar outcomes of locking compression plating and retrograde intramedullary nailing for periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fractures following total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017 Sep;25(9):2921-2928. doi: 10.1007/s00167-016-4050-0. Epub 2016 Feb 20. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017. PMID: 26897137 Review.
Cited by
-
Immediate full weight-bearing, reduced perioperative morbidity and mortality after surgery in the treatment of distal femur fractures using a standard lateral plate plus a helical moulded medial plate ostheosynthesis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025 Feb 1;35(1):60. doi: 10.1007/s00590-025-04176-w. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 39891755
-
Shaft Fractures in Patients Requiring Primary or Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Can Be Successfully Treated with Long-Stemmed Implants without Additional Fixation.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 25;10(21):4926. doi: 10.3390/jcm10214926. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34768444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ehlinger M, Adam P, Abane L, et al. Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2011;19:1473–8. - PubMed
-
- Frigg R, Appenzeller A, Christensen R, et al. The development of the distal femur Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Injury 2001;32 Suppl 3:SC24–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

