Mid age APOE ε4 carriers show memory-related functional differences and disrupted structure-function relationships in hippocampal regions
- PMID: 32080211
- PMCID: PMC7033211
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-59272-0
Mid age APOE ε4 carriers show memory-related functional differences and disrupted structure-function relationships in hippocampal regions
Abstract
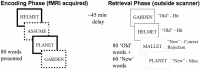
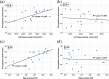
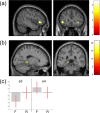
Carriers of the APOE e4 allele are at higher risk of age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease (AD). The underlying neural mechanisms are uncertain, but genotype differences in medial temporal lobe (MTL) functional activity and structure at mid-age might contribute. We tested 16 non-e4 and 16 e4 carriers (aged 45-55) on a subsequent memory task in conjunction with MRI to assess how hippocampal volume (from T1 structural) and microstructure (neurite orientation-dispersion, from NODDI) differs by genotype and in relation to memory encoding. No previous study has investigated APOE effects on hippocampal microstructure using NODDI. Recall performance did not differ by genotype. A genotype by condition interaction in left parahippocampus indicated that in e4 carriers activity did not differentiate subsequently remembered from forgotten words. Hippocampal volumes and microstructure also did not differ by genotype but hippocampal volumes correlated positively with recognition performance in non-e4 carriers only. Similarly, greater hippocampal neurite orientation-dispersion was linked to better recall but only in non-e4s. Thus, we suggest that mid-age e4 carriers show a breakdown of normal MTL activation and structure-performance relationships. This could reflect an inability to utilise compensatory mechanisms, and contribute to higher risk of cognitive decline and AD in later life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

