Prospective diagnostic accuracy study of plasma soluble ST2 for diagnosis of acute aortic syndromes
- PMID: 32080259
- PMCID: PMC7033105
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-59884-6
Prospective diagnostic accuracy study of plasma soluble ST2 for diagnosis of acute aortic syndromes
Abstract
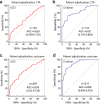
Acute aortic syndromes (AASs) are difficult to diagnose emergencies. Plasma soluble ST2 (sST2), a prognostic biomarker for heart failure, has been proposed as a diagnostic biomarker of AASs outperforming D-dimer, the current diagnostic standard. We performed a prospective diagnostic accuracy study of sST2 for AASs in the Emergency Department (ED). In 2017-2018, patients were enrolled if they had ≥1 red-flag symptoms (chest/abdominal/back pain, syncope, perfusion deficit) and a clinical suspicion of AAS. sST2 was detected with the Presage® assay. Adjudication was based on computed tomography angiography (CTA) or on diagnostic outcome inclusive of 30-day follow-up. 297 patients were enrolled, including 88 with AASs. The median age was 67 years. In 162 patients with CTA, the median sST2 level was 41.7 ng/mL (IQR 29.4-103.2) in AASs and 34.6 ng/mL (IQR 21.4-51.5) in alternative diagnoses (P = 0.005). In ROC analysis, the AUC of sST2 was 0.63, as compared to 0.82 of D-dimer (P < 0.001). Sensitivity and specificity values of sST2 associated with different cutoffs were: 95.5% and 10.8% (≥12 ng/mL), 84.1% and 29.7% (≥23.7 ng/mL), 35.2% and 85.1% (≥66.5 ng/mL). Results were similar in the full cohort. In conclusion, in patients from a European ED, plasma sST2 provided modest accuracy for diagnosis of AASs.
Conflict of interest statement
F.M. reports grant money from the Italian Ministry of Health (GR-2013-02355449, unrelated to the present work), and honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bayer for lectures and educational activities unrelated to the present work. The other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Magnitude of Soluble ST2 as a Novel Biomarker for Acute Aortic Dissection.Circulation. 2018 Jan 16;137(3):259-269. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030469. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29146682
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of the Aortic Dissection Detection Risk Score Plus D-Dimer for Acute Aortic Syndromes: The ADvISED Prospective Multicenter Study.Circulation. 2018 Jan 16;137(3):250-258. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029457. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29030346
-
Accuracy of a diagnostic strategy combining aortic dissection detection risk score and D-dimer levels in patients with suspected acute aortic syndrome.Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2017 Aug;6(5):371-378. doi: 10.1177/2048872615594497. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2017. PMID: 26185259
-
Systematic Review of Aortic Dissection Detection Risk Score Plus D-dimer for Diagnostic Rule-out Of Suspected Acute Aortic Syndromes.Acad Emerg Med. 2020 Oct;27(10):1013-1027. doi: 10.1111/acem.13969. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Acad Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32187432
-
Diagnosis of acute aortic syndromes : imaging and beyond.Herz. 2013 May;38(3):269-76. doi: 10.1007/s00059-012-3710-1. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Herz. 2013. PMID: 23263244 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and management of acute aortic syndromes in the emergency department.Intern Emerg Med. 2021 Jan;16(1):171-181. doi: 10.1007/s11739-020-02354-8. Epub 2020 May 1. Intern Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 32358680 Review.
-
Soluble ST2: A Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Med Sci. 2024 Aug;44(4):669-679. doi: 10.1007/s11596-024-2907-x. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Curr Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39096477 Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of alternative biomarkers for acute aortic syndrome: a systematic review.Emerg Med J. 2024 Oct 23;41(11):678-685. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2023-213772. Emerg Med J. 2024. PMID: 39107052 Free PMC article.
-
Related factors affecting misdiagnosis of aortic dissection: a single-center retrospective study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Apr 14;12:1561225. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1561225. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40297160 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 as outcome predictor after cardiopulmonary resuscitation: an observational prospective study.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 5;11(1):21756. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01389-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34741120 Free PMC article.

