Optogenetic modulation of TDP-43 oligomerization accelerates ALS-related pathologies in the spinal motor neurons
- PMID: 32081878
- PMCID: PMC7035286
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-14815-x
Optogenetic modulation of TDP-43 oligomerization accelerates ALS-related pathologies in the spinal motor neurons
Abstract
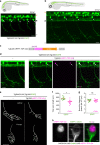
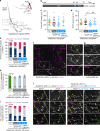
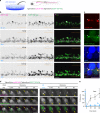
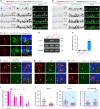
Cytoplasmic aggregation of TDP-43 characterizes degenerating neurons in most cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Here, we develop an optogenetic TDP-43 variant (opTDP-43), whose multimerization status can be modulated in vivo through external light illumination. Using the translucent zebrafish neuromuscular system, we demonstrate that short-term light stimulation reversibly induces cytoplasmic opTDP-43 mislocalization, but not aggregation, in the spinal motor neuron, leading to an axon outgrowth defect associated with myofiber denervation. In contrast, opTDP-43 forms pathological aggregates in the cytoplasm after longer-term illumination and seeds non-optogenetic TDP-43 aggregation. Furthermore, we find that an ALS-linked mutation in the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) exacerbates the light-dependent opTDP-43 toxicity on locomotor behavior. Together, our results propose that IDR-mediated TDP-43 oligomerization triggers both acute and long-term pathologies of motor neurons, which may be relevant to the pathogenesis and progression of ALS.
Conflict of interest statement
A patent application covering this work (application no. JP2018-186569, PCT/JP2019/037829) has been filed in which Inter-University Research Institute Corporation Research Organization of Information and Systems, and K.A. and K.K. are the inventors.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

