Tilted Optic Disc Frequency in Myopia of Different Degree
- PMID: 32082006
- PMCID: PMC7007631
- DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2019.73.391-393
Tilted Optic Disc Frequency in Myopia of Different Degree
Abstract
Introduction: Change in the fundus in myopic patients are often characterized by partially atrophic and tilted optic disc insertions. Due to the altered nerve fiber arrangement, it is more difficult to detect the initial pathological changes of the optic disc. This subject is important because myopia represents well known risk factor for glaucoma.
Aim: This study explored frequency of tilted optic disc in different degree of myopia which has major effect on glaucoma assesment due to unreliable OCTs parameters of the neuroretinal rim in patients with tilted disc.
Methods: Between September 2013 and December 2014, total number of 150 patiens from ophtalmic polyclinic "Dr Sefic" underwent complete ophtalmic examniation. Total of 300 eyes were tested. Patients were separated in 3 groups by diagnosis. Each group was divided by the size of the optic disc diameter into three categories. ANOVA test was used in analysis.
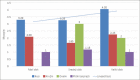
Results: Subjects with tilted disc shape have the highest degree of myopia, and there is a statistically significant difference with other forms of optic disc regardless of the size of the disc itself (p <0.05). The patients with a large disc (4.05 ± 0.65) had the highest degree of myopia in subclass of tilted discs, and these values decreased linearly in relation to the size of the tilted disc.
Conclusion: Myopia height values decreased linearly with respect to the size of the tilted disc.
Keywords: glaucoma; myopia; tilted optic disc.
© 2019 Edita Dervisevic, Nejira Ibrisevic.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shin Hy, Park HY, Park CK. The efect of myopic optic disc tilt on measurement of spectral domain optical coherence tomography parameters. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015;99(1):69–74. - PubMed
-
- Faschinger C, Mossbock G. Myopia and glaucoma. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2007;157(7):173–177. - PubMed
-
- Chang RT, Singh L. Myopia and glaucoma: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2013;24(2):96–101. - PubMed
-
- Detry-Morel MJ. Is myopia a risk factor for glaucoma? Fr Ophthalmol. 2011;34(6):392–395. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical