A Small RNA-Mediated Regulatory Network in Arabidopsis thaliana Demonstrates Connectivity Between phasiRNA Regulatory Modules and Extensive Co-Regulation of Transcription by miRNAs and phasiRNAs
- PMID: 32082334
- PMCID: PMC7001039
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01710
A Small RNA-Mediated Regulatory Network in Arabidopsis thaliana Demonstrates Connectivity Between phasiRNA Regulatory Modules and Extensive Co-Regulation of Transcription by miRNAs and phasiRNAs
Abstract
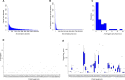
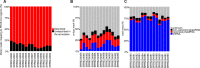
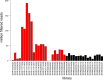
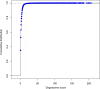
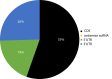
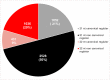
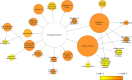
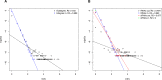
Gene regulation involves the orchestrated action of multiple regulators to fine-tune the expression of genes. Hierarchical interactions and co-regulation among regulators are commonly observed in biological systems, leading to complex regulatory networks. Small RNA (sRNAs) have been shown to be important regulators of gene expression due to their involvement in multiple cellular processes. In plants, microRNA (miRNAs) and phased small interfering RNAs (phasiRNAs) correspond to two well-characterized types of sRNAs involved in the regulation of posttranscriptional gene expression, although information about their targets and interactions with other gene expression regulators is limited. We describe an extended sRNA-mediated regulatory network in Arabidopsis thaliana that provides a reference frame to understand sRNA biogenesis and activity at the genome-wide level. This regulatory network combines a comprehensive evaluation of phasiRNA production and sRNA targets supported by degradome data. The network includes ~17% of genes in the A. thaliana genome, representing ~50% annotated gene ontology (GO) functional categories. Approximately 14% of genes with GO annotations corresponding to regulation of gene expression were found to be under sRNA control. The unbiased bioinformatic approach used to produce the network was able to detect 107 PHAS loci (regions of phasiRNA production), 5,047 active phasiRNAs (~70% of which were non-canonical), and reconstruct 17 regulatory modules resulting from complex regulatory interactions between different sRNA-regulatory pathways. Known regulatory modules like miR173-TAS-PPR/TPR and miR390-TAS3-ARF/F-box were faithfully reconstructed and expanded, illustrating the accuracy and sensitivity of the methods and providing confidence for the validity of findings of previously unrecognized modules. The network presented here includes a 2X increase in the number of identified PHAS loci, a large complement (~70%) of non-canonical phasiRNAs, and the most comprehensive evaluation of sRNA cleavage activity in A. thaliana to date. Structural analysis showed similarities to networks of other biological systems and demonstrated connectivity between phasiRNA regulatory modules with extensive co-regulation of transcripts by miRNAs and phasiRNAs. The described regulatory network provides a reference that will facilitate global analyses of individual plant regulatory programs such as those that control homeostasis, development, and responses to biotic and abiotic environmental changes.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; degradome; miRNA; network; phasiRNA; regulation.
Copyright © 2020 Vargas-Asencio and Perry.
Figures

References
-
- Albert R. (2005). Scale-free networks in cell biology. J. Cell Sci. 118, 4947–4957. Available at: http://jcs.biologists.org/content/118/21/4947.abstract. 10.1242/jcs.02714 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boccara M., Sarazin A., Thiébeauld O., Jay F., Voinnet O., Navarro L., et al. (2014). The Arabidopsis miR472-RDR6 silencing pathway modulates PAMP- and effector-triggered immunity through the post-transcriptional control of disease resistance genes. PloS Pathog. 10, e1003883. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003883 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

