MiR-199b-5p Suppresses Tumor Angiogenesis Mediated by Vascular Endothelial Cells in Breast Cancer by Targeting ALK1
- PMID: 32082362
- PMCID: PMC7002562
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01397
MiR-199b-5p Suppresses Tumor Angiogenesis Mediated by Vascular Endothelial Cells in Breast Cancer by Targeting ALK1
Abstract
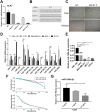
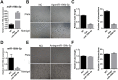
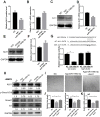
Angiogenesis is a crucial event during cancer progression that regulates tumor growth and metastasis. Activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1), predominantly expressed in endothelial cells, plays a key role in the organization of neo-angiogenic vessels. Therapeutic targeting of ALK1 has been proposed as a promising strategy for cancer treatment, and microRNAs (miRNAs) are increasingly being explored as modulators of angiogenesis. However, the regulation of ALK1 by miRNAs is unclear. In this study, we identified that ALK1 is directly targeted by miR-199b-5p, which was able to inhibit angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, it was found that miR-199b-5p was repressed in breast cancer cells and its expression was decreased during the VEGF-induced angiogenesis process of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Overexpression of miR-199b-5p inhibited the formation of capillary-like tubular structures and migration of HUVECs. Furthermore, overexpression of miR-199b-5p inhibited the mRNA and protein expression of ALK1 in HUVECs by directly binding to its 3'UTR. Additionally, overexpression of miR-199b-5p attenuated the induction of ALK1/Smad/Id1 pathway by BMP9 in HUVECs. Finally, overexpression of miR-199b-5p reduced tumor growth and angiogenesis in in vivo. Taken together, these findings demonstrate the anti-angiogenic role of miR-199b-5p, which directly targets ALK1, suggesting that miR-199b-5p might be a potential anti-angiogenic target for cancer therapy.
Keywords: ALK1; HUVECs; angiogenesis; breast cancer; miR-199b-5p; tumor growth.
Copyright © 2020 Lin, Qiu, Xiao, Ma, Xu, Zhang, Gao, Chen, Li, Li and Qian.
Figures



Similar articles
-
miR-199b-5p-AKAP1-DRP1 Pathway Plays a Key Role in ox-LDL-induced Mitochondrial Fission and Endothelial Apoptosis.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022;23(13):1612-1622. doi: 10.2174/1389201023666220324123224. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35331106
-
Role of miR-199b-5p in regulating angiogenesis in mouse myocardial microvascular endothelial cells through HSF1/VEGF pathway.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Oct;47:142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27689811
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 regulates microRNAs miR-494 and miR-126-5p in control of endothelial cell function in angiogenesis.Thromb Haemost. 2017 Apr 3;117(4):734-749. doi: 10.1160/TH16-08-0643. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28124060
-
Activin receptor-like kinase 1 as a target for anti-angiogenesis therapy.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013 Nov;22(11):1371-83. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2013.837884. Epub 2013 Sep 21. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013. PMID: 24053899 Review.
-
The Dual Effect of the BMP9-ALK1 Pathway in Blood Vessels: An Opportunity for Cancer Therapy Improvement?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 28;13(21):5412. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215412. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771575 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oncosuppressive miRNAs loaded in lipid nanoparticles potentiate targeted therapies in BRAF-mutant melanoma by inhibiting core escape pathways of resistance.Oncogene. 2023 Jan;42(4):293-307. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02547-9. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36418472 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_ZFR affects FABP7 expression to regulate breast cancer progression by acting as a sponge for miR-223-3p.Thorac Cancer. 2022 May;13(9):1369-1380. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14401. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Thorac Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35355424 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of microRNA-199b as A Promising Predictor of Outcome and Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 5;13(19):5003. doi: 10.3390/cancers13195003. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638487 Free PMC article.
-
miR-199b-5p-DDR1-ERK signalling axis suppresses prostate cancer metastasis via inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Br J Cancer. 2021 Mar;124(5):982-994. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-01187-8. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Br J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33239676 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer cell-secreted miR-199b-5p hijacks neurometabolic coupling to promote brain metastasis.Nat Commun. 2024 May 29;15(1):4549. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48740-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38811525 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

