The Functional Severity Assessment of Coronary Stenosis Using Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography-Based Myocardial Mass at Risk and Minimal Lumen Diameter
- PMID: 32082419
- PMCID: PMC7013296
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6716130
The Functional Severity Assessment of Coronary Stenosis Using Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography-Based Myocardial Mass at Risk and Minimal Lumen Diameter
Abstract
Background: We investigated whether or not the addition of myocardial mass at risk (MMAR) to quantitative coronary angiography was useful for diagnosing functionally significant coronary stenosis in the daily practice.
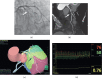
Methods: We retrospectively enrolled 111 consecutive patients with 149 lesions who underwent clinically indicated coronary computed tomography angiography and subsequent elective coronary angiography with fractional flow reserve (FFR) measurement. MMAR was calculated using a workstation-based software program with ordinary thin slice images acquired for the computed tomography, and the minimal lumen diameter (MLD) and the diameter stenosis were measured with quantitative coronary angiography.
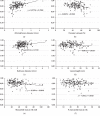
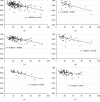
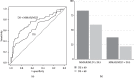
Results: The MLD and MMAR were significantly correlated with the FFR, and the MMAR-to-MLD ratio (MMAR/MLD) showed a good correlation. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of MMAR/MLD for FFR ≤ 0.8 was 0.746, and the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were 60%, 83%, 68%, and 77%, respectively, at a cut-off value of 29.5 ml/mm. The addition of MMAR/MLD to diameter stenosis thus made it possible to further discriminate lesions with FFR ≤ 0.8 (AUC = 0.750). For the proximal left coronary artery lesions, in particular, MMAR/MLD showed a better correlation with the FFR, and the AUC of MMAR/MLD for FFR ≤ 0.8 was 0.919 at a cut-off value of 31.7 ml/mm.
Conclusions: The index of MMAR/MLD correlated well with the physiological severity of coronary stenosis and showed good accuracy for detecting functional significance. The MMAR/MLD might be a useful parameter to consider when deciding the indication for revascularization.
Copyright © 2020 Kenji Sadamatsu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Ueno T received a research grant from Abbott Vascular. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Montalescot G., Sechtem U., Achenbach S., et al. ESC guidelines on the management of stable coronary artery disease: the task force on the management of stable coronary artery disease of the European society of cardiology. European Heart Journal. 2013;34(38):2949–3003. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht296. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Windecker S., Kolh P., Alfonso F., et al. ESC/EACTS guidelines on myocardial revascularization: the task force on myocardial revascularization of the European society of cardiology (ESC) and the European association for cardio-thoracic surgery (EACTS) developed with the special contribution of the European association of percutaneous cardiovascular interventions (EAPCI) European Heart Journal. 2014;35(37):2541–2619. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu278. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Okahara A., Mine D., Sadamatsu K. Catastrophic acute thrombotic occlusion during fractional flow reserve measurement. Journal of Medical Cases. 2015;6(6):279–281. doi: 10.14740/jmc2174w. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

