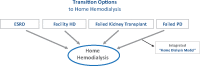
Integrated care: enhancing transition from renal replacement therapy options to home haemodialysis
- PMID: 32082558
- PMCID: PMC7025339
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfz140
Integrated care: enhancing transition from renal replacement therapy options to home haemodialysis
Abstract
Transition is an intrinsic process in the life of a patient with kidney disease and should be planned and anticipated when possible. A single therapy option might not be adequate across a patient's entire lifespan and many patients will require a switch in their treatment modality to adapt the treatment to their clinical and psychosocial needs. There are several reasons behind changing a patient's treatment modality, and the consequences of each decision should be evaluated, considering both short- and long-term benefits and risks. Dialysis modality transition is not only to allow for technical optimization or improved patient survival, the patient's experience associated with the transition should also be taken into account. Transition should not be considered as treatment failure, but rather as an expected progression in the patient's treatment options.
Keywords: home haemodialysis; integrated home dialysis model; planned transition; renal replacement therapy; transition.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
References
-
- Covic A, Bammens B, Lobbedez T. et al. Educating end-stage renal disease patients on dialysis modality selection: clinical advice from the European Renal Best Practice (ERBP) Advisory Board. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2010; 25: 1757–1759 - PubMed
-
- Moist LM, Lok CE.. Incident dialysis access in patients with end-stage kidney disease: what needs to be improved. Semin Nephrol 2017; 37: 151–158 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources