Immediate Effects and Acceptability of an Application-Based Stretching Exercise Incorporating Deep Slow Breathing for Neck Pain Self-management
- PMID: 32082700
- PMCID: PMC7010943
- DOI: 10.4258/hir.2020.26.1.50
Immediate Effects and Acceptability of an Application-Based Stretching Exercise Incorporating Deep Slow Breathing for Neck Pain Self-management
Abstract
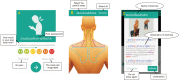
Objectives: This study evaluated the immediate effects and acceptability of a smartphone application named NeckProtector to promote neck pain self-management through stretching incorporating deep slow breathing, among smartphone users with neck pain.
Methods: One-hundred participants were recruited in the study. Participants were divided into two groups by block randomized allocation. The researchers gave the NeckProtector application to all participants for acceptability testing by navigation of the application for 20-30 minutes. Next, the treatment group (n = 50) conducted the exercise program via smartphone application for 15-20 minutes, while the control group (n = 50) rested for 20 minutes. Evaluations were performed at baseline and after intervention for pain intensity, muscle tension, pressure pain threshold (PPT), and cervical range of motion (CROM). Quantitative and qualitative feedback was then obtained by an acceptability survey and open-ended questionnaires.
Results: The immediate effects showed statistically significant improvements in pain intensity, muscle tension, PPT, and CROM in the treatment group in comparison to the control group. Participants reported a high level of acceptability through ratings on a Likert scale. The qualitative questionnaires received positive responses that the application was easy to use and the exercise program was useful to cope with neck pain.
Conclusions: NeckProtector can be an alternative treatment for neck pain self-management via smartphone application among smartphone users with neck pain. Further studies should examine the long-term effectiveness (Clinical trials registry: TCTR20160523001).
Keywords: Breathing Exercises; Mobile Applications; Muscle Stretching Exercises; Neck Pain; Self-Management.
© 2020 The Korean Society of Medical Informatics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Manual treatment for cervicogenic headache and active trigger point in the sternocleidomastoid muscle: a pilot randomized clinical trial.J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2013 Sep;36(7):403-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jmpt.2013.05.022. Epub 2013 Jul 8. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23845200 Clinical Trial.
-
Immediate changes in widespread pressure pain sensitivity, neck pain, and cervical range of motion after cervical or thoracic thrust manipulation in patients with bilateral chronic mechanical neck pain: a randomized clinical trial.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012 Sep;42(9):806-14. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2012.4151. Epub 2012 Jun 18. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012. PMID: 22711239 Clinical Trial.
-
Feasibility of a Smartphone-Based Exercise Program for Office Workers With Neck Pain: An Individualized Approach Using a Self-Classification Algorithm.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017 Jan;98(1):80-87. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017. PMID: 27693421
-
Comparison of miniscalpel-needle release, acupuncture needling, and stretching exercise to trigger point in myofascial pain syndrome.Clin J Pain. 2010 Mar-Apr;26(3):251-7. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181b8cdc8. Clin J Pain. 2010. PMID: 20173440 Clinical Trial.
-
Muscle stretching with deep and slow breathing patterns: a pilot study for therapeutic development.J Complement Integr Med. 2018 Aug 22;16(2):/j/jcim.2019.16.issue-2/jcim-2017-0167/jcim-2017-0167.xml. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2017-0167. J Complement Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 30133419 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Functional assessment and evaluation of health problems with the cervical spine among dental assistants and hygienists.Postep Psychiatr Neurol. 2023 Jun;32(2):68-75. doi: 10.5114/ppn.2023.129053. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Postep Psychiatr Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37497201 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Trapezius Muscle Self-Stretching on Muscle Stiffness and Choroidal Circulatory Dynamics: An Evaluation Using Ultrasound Strain Elastography and Laser Speckle Flowgraphy.Tomography. 2025 Jun 25;11(7):73. doi: 10.3390/tomography11070073. Tomography. 2025. PMID: 40710891 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of 25 Years of Mobile Health Tools for Pain Management in Patients With Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Aug 16;26:e59358. doi: 10.2196/59358. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39150748 Free PMC article.
-
mHealth Intervention for Improving Pain, Quality of Life, and Functional Disability in Patients With Chronic Pain: Systematic Review.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2023 Feb 2;11:e40844. doi: 10.2196/40844. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2023. PMID: 36729570 Free PMC article.
-
Telehealth and Virtual Reality Technologies in Chronic Pain Management: A Narrative Review.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024 Mar;28(3):83-94. doi: 10.1007/s11916-023-01205-3. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024. PMID: 38175490 Review.
References
-
- Sarwar M, Soomro TR. Impact of smartphone's on society. Eur J Sci Res. 2013;98(2):216–226.
-
- Statista. Number of smartphone users in Thailand from 2013 to 2021 [Internet] New York (NY): Statista; 2017. [cited at 2020 Jan 7]. Available from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/467191/forecast-of-smartphone-users-....
-
- Poushter J. Smartphone ownership and Internet usage continues to climb in emerging economies [Internet] Washington (DC): Pew Research Center; 2016. [cited at 2020 Jan 7]. Available from: http://www.pewglobal.org/2016/02/22/smartphone-ownership-and-internet-us...
-
- Berolo S, Wells RP, Amick BC., 3rd Musculoskeletal symptoms among mobile hand-held device users and their relationship to device use: a preliminary study in a Canadian university population. Appl Ergon. 2011;42(2):371–378. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

