Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for early renal failure under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for postcardiotomy shock
- PMID: 32082878
- PMCID: PMC7021425
- DOI: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2019.17891
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for early renal failure under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for postcardiotomy shock
Abstract
Background: This study aims to investigate the relationship between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and renal injury in patients under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for postcardiotomy shock.
Methods: Between January 2007 and July 2018, a total of 119 patients (38 males, 81 females; mean age 54.4±13.0 years; range, 24 to 74 years) who received extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for postcardiotomy shock and survived at least 48 hours in our center were retrospectively analyzed. Pre- and postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios, demographic characteristics, renal function parameters, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenationrelated data of the patients were recorded. Occurrence and stages of renal injury was determined using the revised Acute Kidney Injury Network and Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes criteria.
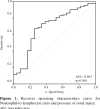
Results: No significant relationship was found between preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and renal injury (p>0.05). Postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio was higher in patients who developed renal injury, compared to patients without renal injury (8.68 [0.84-42.00] vs. 4.02 [1.04-21.21], respectively, p=0.004). When patients were grouped for renal injury stage according to the revised Acute Kidney Injury Network (p=0.015) and Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (p=0.006) criteria, the patients with more severe renal injury had higher neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. The receiver operating characteristics analysis revealed a cut-off value of 6.71 for the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for the detection of renal injury. Patients with a value above 6.71 had an odds ratio of 5.941 for occurrence of renal injury.
Conclusion: Postoperative, but not preoperative neutrophil-tolymphocyte ratio is associated with presence and severity of renal injury in patients under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for postcardiotomy shock. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a simple and inexpensive marker of inflammation in this patient population.
Keywords: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; inflammation; neutrophilto- lymphocyte ratio; postcardiotomy shock; renal injury.
Copyright © 2019, Turkish Society of Cardiovascular Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Cheng R, Hachamovitch R, Kittleson M, Patel J, Arabia F, Moriguchi J, et al. Complications of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for treatment of cardiogenic shock and cardiac arrest: a meta-analysis of 1,866 adult patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97:610–616. - PubMed
-
- Hsiao CC, Chang CH, Fan PC, Ho HT, Jenq CC, Kao KC, et al. Prognosis of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: the impact of urine output on mortality. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97:1939–1944. - PubMed
-
- Chen YC, Tsai FC, Chang CH, Lin CY, Jenq CC, Juan KC, et al. Prognosis of patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: the impact of acute kidney injury on mortality. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;91:137–142. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources