A Multi-Task Group Bi-LSTM Networks Application on Electrocardiogram Classification
- PMID: 32082952
- PMCID: PMC7028438
- DOI: 10.1109/JTEHM.2019.2952610
A Multi-Task Group Bi-LSTM Networks Application on Electrocardiogram Classification
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of death globally. Electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis can provide thoroughly assessment for different CVDs efficiently. We propose a multi-task group bidirectional long short-term memory (MTGBi-LSTM) framework to intelligent recognize multiple CVDs based on multi-lead ECG signals.
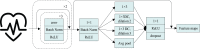
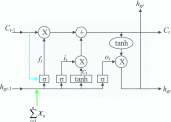
Methods: This model employs a Group Bi-LSTM (GBi-LSTM) and Residual Group Convolutional Neural Network (Res-GCNN) to learn the dual feature representation of ECG space and time series. GBi-LSTM is divided into Global Bi-LSTM and Intra-Group Bi-LSTM, which can learn the features of each ECG lead and the relationship between leads. Then, through attention mechanism, the different lead information of ECG is integrated to make the model to possess the powerful feature discriminability. Through multi-task learning, the model can fully mine the association information between diseases and obtain more accurate diagnostic results. In addition, we propose a dynamic weighted loss function to better quantify the loss to overcome the imbalance between classes.
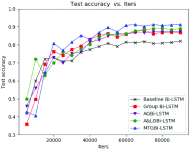
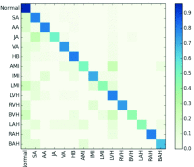
Results: Based on more than 170,000 clinical 12-lead ECG analysis, the MTGBi-LSTM method achieved accuracy, precision, recall and F1 of 88.86%, 90.67%, 94.19% and 92.39%, respectively. The experimental results show that the proposed MTGBi-LSTM method can reliably realize ECG analysis and provide an effective tool for computer-aided diagnosis of CVD.
Keywords: ECG; attention mechanism; bidirectional long short-term memory network; multi-task learning.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization, Mendis S., Puska P., and Norrving B., Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2011, pp. 3–18.
-
- McGill H. C., McMahan C. A., and Gidding S. S., “Preventing heart disease in the 21st century: Implications of the pathobiological determinants of atherosclerosis in youth (PDAY) study,” Circulation, vol. 117, no. 9, pp. 1216–1227, Mar. 2008. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

