The Relation between Hearing Loss and Smoking among Workers Exposed to Noise, Using Linear Mixed Models
- PMID: 32083026
- PMCID: PMC7007995
- DOI: 10.22038/ijorl.2019.37555.2229
The Relation between Hearing Loss and Smoking among Workers Exposed to Noise, Using Linear Mixed Models
Abstract
Introduction: Noise is one of the most common and harmful physical factors in the working environment and has physical and psychological effects on individuals. In this study, the audiometry results of industrial workers were modeled and the effect of noise and other factors on hearing loss was examined.
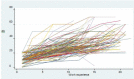
Materials and methods: This was a longitudinal study based on the records of workers who had worked over 10 years in the industry and had recorded audiometries since their employment. Data was analyzed through linear mixed models.
Results: During each year of noise exposure, hearing loss was 1.9 db at 4000 Hz; 0.059 in low frequencies and 0.62 db in high frequencies. At 8000 Hz the effect of the age at employment on hearing loss was significant (P=0.014). At low frequencies the interaction of smoking and age at employment was significantly related to hearing loss (P˂0.001).
Conclusion: This study showed that despite acquaintance with safety measures, workers still face hearing loss in industry and employers should put workers under more surveillance for using protective gear. Smoking might be another risk factor for hearing loss.
Keywords: Hearing Loss; Linear Models; Longitudinal Studies; Noise-Induced.
Figures
References
-
- Behnoodi Z. Environmental Health and Safety. 2nd edition. Tehran: Boshra Publishers; 2004.
-
- Valipour Marghamlaki E, Abedi K, Rahiminejad M, Soltani Zamani M, Jalali J. Proceeding of National symposium of Noise, Health and Development. Kashan; Iran: 2003. Rates of hearing loss employees of Shahid Beheshti Airport of Isfahan.
-
- Bagheri Hosseinabadi M, Khanjani N, Münzel T, Daiber A, Yaghmorloo M. Chronic Occupational Noise Exposure: Effects on DNA Damage, Blood Pressure, and Serum Biochemistry. Mutat Res. 2019:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Ghotbi MR, Khanjani N, Barkhordari A, Rahimi Moghadam S, Mozaffari A, Gozashti MH. Changes in urinary catecholamines in response to noise exposure in workers at Sarcheshmeh Copper Complex, Kerman, Iran. Environ Monit Assess, . 2013;185(11):p. 8809–14. - PubMed
-
- Rahimi Moghadam S, Laiegh Tizabi MN, Khanjani N, Emkani M, Taghavi Manesh V, Mohammadi AA, et al. Noise pollution and sleep disturbance among Neyshabur Hospital staff, Iran (2015) J Occup Health Epidemiol, 2018;7(1):53–64.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous