Identification and Distribution of Pathogens in a Major Tertiary Hospital of Indonesia
- PMID: 32083046
- PMCID: PMC7006218
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2019.00395
Identification and Distribution of Pathogens in a Major Tertiary Hospital of Indonesia
Abstract
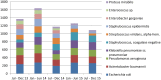
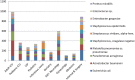
The nosocomial persistence of multiple drug resistance organisms constitutes a global threat. Healthcare-setting acquired infections are subject to substantial selection pressure and are frequently associated with drug resistance. As part of the microbiological surveillance of the Sanglah tertiary referral hospital in the island province of Bali, the distribution of bacterial pathogen and their relative susceptibilities were recorded over a 30 months period. This is the first such detailed study benchmarking the type and sensitivity of bacterial pathogens in a major tertiary referral hospital within Indonesia and it is hoped that it will lead to similar reports in the near future, while informing local and national antimicrobial stewardship policies.
Keywords: Indonesia; drug resistance; multi-drug-resistance organisms; pathogen distribution; tertiary hospital.
Copyright © 2020 Budayanti, Aisyah, Fatmawati, Tarini, Kozlakidis and Adisasmito.
Figures
References
-
- Wu T-C. Carbapenem-resistant or multidrug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii-a clinician's perspective. Multidrug-Resistant Bacter. (2011) 16:6 Available online at: http://www.fmshk.org/database/articles/03mb1_17.pdf (accessed December 16, 2019).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials