Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 Regulates the Stability of Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein
- PMID: 32083080
- PMCID: PMC7005485
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00026
Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 Regulates the Stability of Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein
Abstract
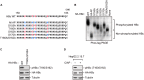
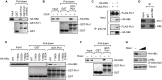
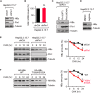
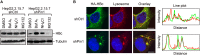
The dynamic interplay between virus and host proteins is critical for establishing efficient viral replication and virus-induced pathogenesis. Phosphorylation-dependent prolyl isomerization by Pin1 provides a unique mechanism of molecular switching to control both protein function and stability. We demonstrate here that Pin1 binds and stabilizes hepatitis B virus core protein (HBc) in a phosphorylation-dependent manner, and promotes the efficient viral propagation. Phos-tag gel electrophoresis with various site-directed mutants of HBc revealed that Thr160 and Ser162 residues within the C terminal arginine-rich domain are phosphorylated concomitantly. GST pull-down assay and co-immunoprecipitation analysis demonstrated that Pin1 associated with phosphorylated HBc at the Thr160-Pro and Ser162-Pro motifs. Chemical or genetic inhibition of Pin1 significantly accelerated the rapid degradation of HBc via a lysosome-dependent pathway. Furthermore, we found that the pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase catalytic subunit 2 (PDP2) could dephosphorylate HBc at the Pin1-binding sites, thereby suppressing Pin1-mediated HBc stabilization. Our findings reveal an important regulatory mechanism of HBc stability catalyzed by Pin1 and may facilitate the development of new antiviral therapeutics targeting Pin1 function.
Keywords: hepatitis B virus; lysosome; phosphorylation; prolyl isomerization; virus-host interaction.
Copyright © 2020 Nishi, Miyakawa, Matsunaga, Khatun, Yamaoka, Watashi, Sugiyama, Kimura, Wakita and Ryo.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

