Impact of Raltegravir or Efavirenz on Cell-Associated Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Deoxyribonucleic Acid and Systemic Inflammation in HIV-1/Tuberculosis Coinfected Adults Initiating Antiretroviral Therapy
- PMID: 32083147
- PMCID: PMC7019658
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofz549
Impact of Raltegravir or Efavirenz on Cell-Associated Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Deoxyribonucleic Acid and Systemic Inflammation in HIV-1/Tuberculosis Coinfected Adults Initiating Antiretroviral Therapy
Abstract
Background: In view of the fast viremia decline obtained with integrase inhibitors, we studied the respective effects of initiating efavirenz (EFV) or raltegravir (RAL)-based antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimens on human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) levels and inflammation biomarkers in the highly inflammatory setting of advanced HIV-1 disease with tuberculosis (TB) coinfection.
Methods: We followed cell-associated HIV-1 DNA, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), interleukin 6 (IL-6), soluble CD14 and D-Dimer levels for 48 weeks after ART initiation in the participants to the ANRS12-180 REFLATE-TB study. This phase II open-label randomized study included ART-naive people with HIV and TB treated with rifampicin to receive RAL 400 mg twice daily (RAL400), RAL 800 mg twice daily (RAL800) or EFV 600 mg QD with tenofovir and lamivudine.
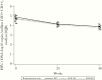
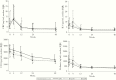
Results: In 146 participants, the median (interquartile range [IQR]) week (W)0 HIV-1 DNA level was 4.7 (IQR, 4.3-5.1) log10 copies/106 CD4+, and the reduction by W48 was -0.8 log10 copies/106 CD4+ on EFV, -0.9 on RAL400, and -1.0 on RAL800 (P = .74). Baseline median (IQR) hsCRP, IL-6, sCD14, and D-Dimer levels were 6.9 (IQR, 3.3-15.6) mg/L, 7.3 (IQR, 3.5-12.3) pg/mL, 3221 (IQR, 2383-4130) ng/mL, and 975 (IQR, 535-1970) ng/mL. All biomarker levels decreased over the study: the overall W0-W48 mean (95% confidence interval) fold-change on ART was 0.37 (IQR, 0.28-0.48) for hsCRP, 0.42 (IQR, 0.35-0.51) for IL-6, 0.51 (IQR, 0.47-0.56) for sCD14, and 0.39 (IQR, 0.32-0.47) for D-Dimers. There were no differences in biomarker reduction across treatment arms.
Conclusions: In participants with HIV and TB, EFV, RAL400, or RAL800 effectively and equally reduced inflammation and HIV-1 DNA levels.
Keywords: HIV integrase inhibitors; HIV-1 DNA; inflammation; raltegravir; tuberculosis.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Reynolds HE, Chrdle A, Egan D, et al. . Effect of intermittent rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics and safety of raltegravir. J Antimicrob Chemother 2015; 70:550–4. - PubMed
-
- Grinsztejn B, De Castro N, Arnold V, et al. ; ANRS 12 180 Reflate TB study group Raltegravir for the treatment of patients co-infected with HIV and tuberculosis (ANRS 12 180 Reflate TB): a multicentre, phase 2, non-comparative, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2014; 14:459–67. - PubMed
-
- Taburet AM, Sauvageon H, Grinsztejn B, et al. . Pharmacokinetics of raltegravir in HIV-infected patients on rifampicin-based antitubercular therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2015; 61:1328–35. - PubMed
-
- Achhra AC, Phillips A, Emery S, et al. ; International Network for Strategic Initiatives in Global HIV Trials (INSIGHT) Strategic Management of Antiretroviral Therapy (SMART) and Flexible Initial Retrovirus Suppressive Therapies (FIRST) study groups Pre-therapy inflammation and coagulation activation and long-term CD4 count responses to the initiation of antiretroviral therapy. HIV Med 2015; 16:449–54. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

