A Deep Learning Approach to Antibiotic Discovery
- PMID: 32084340
- PMCID: PMC8349178
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.01.021
A Deep Learning Approach to Antibiotic Discovery
Erratum in
-
A Deep Learning Approach to Antibiotic Discovery.Cell. 2020 Apr 16;181(2):475-483. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.001. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32302574 No abstract available.
Abstract
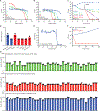
Due to the rapid emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, there is a growing need to discover new antibiotics. To address this challenge, we trained a deep neural network capable of predicting molecules with antibacterial activity. We performed predictions on multiple chemical libraries and discovered a molecule from the Drug Repurposing Hub-halicin-that is structurally divergent from conventional antibiotics and displays bactericidal activity against a wide phylogenetic spectrum of pathogens including Mycobacterium tuberculosis and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Halicin also effectively treated Clostridioides difficile and pan-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections in murine models. Additionally, from a discrete set of 23 empirically tested predictions from >107 million molecules curated from the ZINC15 database, our model identified eight antibacterial compounds that are structurally distant from known antibiotics. This work highlights the utility of deep learning approaches to expand our antibiotic arsenal through the discovery of structurally distinct antibacterial molecules.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; antibiotic tolerance; antibiotics; drug discovery; machine learning.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests J.J.C. is scientific co-founder and SAB chair of EnBiotix, an antibiotic drug discovery company.
Figures
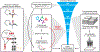


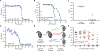

Comment in
-
Parsing Molecules for Drug Discovery.Biochemistry. 2020 May 5;59(17):1645-1646. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00278. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32315170 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Balaban NQ, Helaine S, Lewis K, Ackermann M, Aldridge B, Andersson DI, Brynildsen MP, Bumann D, Camilli A, Collins JJ, Dehio C, Fortune S, Ghigo JM, Hardt WD, Harms A, Heinemann M, Hung DT, Jenal U, Levin BR, Michiels J, Storz G, Tan MW, Tenson T, Van Melderen L, Zinkernagel A, 2019. Definitions and guidelines for research on antibiotic persistence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 17, 441–448. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown DG, May-Dracka TL, Gagnon MM, Tommasi R, 2014. Trends and exceptions of physical properties on antibacterial activity for Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. J. Med. Chem 57, 10144–10161. - PubMed
-
- Brown ED, Wright GD, 2016. Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature 529, 336–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

