Hydrogen Sulfide in Pharmacotherapy, Beyond the Hydrogen Sulfide-Donors
- PMID: 32085474
- PMCID: PMC7072623
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10020323
Hydrogen Sulfide in Pharmacotherapy, Beyond the Hydrogen Sulfide-Donors
Abstract
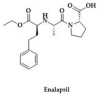
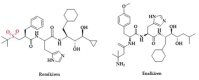
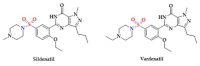
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is one of the important biological mediators involved in physiological and pathological processes in mammals. Recently developed H2S donors show promising effects against several pathological processes in preclinical and early clinical studies. For example, H2S donors have been found to be effective in the prevention of gastrointestinal ulcers during anti-inflammatory treatment. Notably, there are well-established medicines used for the treatment of a variety of diseases, whose chemical structure contains sulfur moieties and may release H2S. Hence, the therapeutic effect of these drugs may be partly the result of the release of H2S occurring during drug metabolism and/or the effect of these drugs on the production of endogenous hydrogen sulfide. In this work, we review data regarding sulfur drugs commonly used in clinical practice that can support the hypothesis about H2S-dependent pharmacotherapeutic effects of these drugs.
Keywords: H2S donors; H2S pro-drugs; anti-inflammatory agents; anticancer drug; cardiovascular; hydrogen sulfide; neuromodulation; sulfur-containing drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






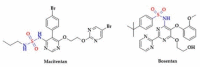


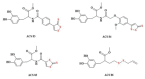





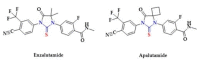
References
-
- Kombian S.B., Warenycia M.W., Mele F.G., Reiffenstein R.J. Effects of acute intoxication with hydrogen sulfide on central amino acid transmitter systems. Neurotoxicology. 1988;9:587–595. - PubMed
-
- Warenycia M.W., Goodwin L.R., Benishin C.G., Reiffenstein R.J., Francom D.M., Taylor J.D., Dieken F.P. Acute hydrogen sulfide poisoning. Demonstration of selective uptake of sulfide by the brainstem by measurement of brain sulfide levels. Biochem. Pharm. 1989;38:973–981. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90288-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

