pH-Sensitive Mixed Micelles Assembled from PDEAEMA-PPEGMA and PCL-PPEGMA for Doxorubicin Delivery: Experimental and DPD Simulations Study
- PMID: 32085488
- PMCID: PMC7076365
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12020170
pH-Sensitive Mixed Micelles Assembled from PDEAEMA-PPEGMA and PCL-PPEGMA for Doxorubicin Delivery: Experimental and DPD Simulations Study
Abstract
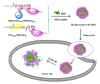
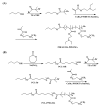
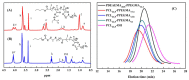
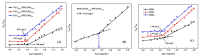
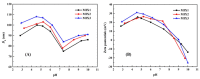
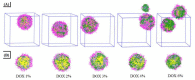
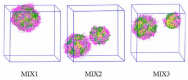
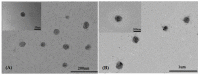
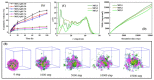
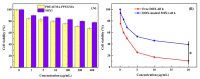
To decrease critical micelle concentration (CMC), improve stability, and keep high drug-loading capacity, three pH-sensitive mixed micelles applied for anticancer drug controlled delivery were prepared by the mixture of polymers poly (N,N-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate)-b-poly(poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate) (PDEAEMA-PPEGMA) and polycaprolactone-b-poly (poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate) (PCL-PPEGMA), which were synthesized and confirmed by 1H NMR and gel permeation chromatographic (GPC). The critical micelle concentration (CMC) values of the prepared mixed micelles were low, and the micellar sizes and zeta potentials of the blank mixed micelles demonstrated good pH-responsive behavior. Combined experimental techniques with dissipative particle dynamics (DPD) simulation, the particle sizes, zeta potentials, drug loading content (LC), encapsulation efficiency (EE), aggregation morphologies, and doxorubicin (DOX) distribution of the mixed micelles were investigated, and the high DOX-loading capacity of the mixed micelles was found. Both in vitro DOX release profiles and DPD simulations of the DOX dynamics release process exhibited less leakage and good stability in neutral conditions and accelerated drug release behavior with a little initial burst in slightly acidic conditions. Cytotoxicity tests showed that the polymer PDEAEMA-PPEGMA and the blank mixed micelles had good biocompatibility, and DOX-loaded mixed micelles revealed certain cytotoxicity. These results suggest that the drug-loaded mixed micelles that consisted of the two polymers PDEAEMA-PPEGMA and PCL-PPEGMA can be new types of pH-responsive well-controlled release anticancer drug delivery mixed micelles.
Keywords: dissipative particle dynamics simulation; drug delivery system; mixed micelles; pH-responsive; well-controlled release.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DPD simulations and experimental study on reduction-sensitive polymeric micelles self-assembled from PCL-SS-PPEGMA for doxorubicin controlled release.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021 Aug;204:111797. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111797. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021. PMID: 33957490
-
Amphiphilic miktoarm star copolymer (PCL)3-(PDEAEMA-b-PPEGMA)3 as pH-sensitive micelles in the delivery of anticancer drug.J Mater Chem B. 2014 Jul 7;2(25):4008-4020. doi: 10.1039/c3tb21694b. Epub 2014 May 23. J Mater Chem B. 2014. PMID: 32261652
-
DPD simulations on mixed polymeric DOX-loaded micelles assembled from PCL-SS-PPEGMA/PDEA-PPEGMA and their dual pH/reduction-responsive release.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021 Sep 14;23(34):19011-19021. doi: 10.1039/d1cp02750f. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021. PMID: 34612439
-
Dissipative particle dynamics studies of doxorubicin-loaded micelles assembled from four-arm star triblock polymers 4AS-PCL-b-PDEAEMA-b-PPEGMA and their pH-release mechanism.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Oct 31;117(43):13688-97. doi: 10.1021/jp407529u. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 24079339
-
DPD studies on mixed micelles self-assembled from MPEG-PDEAEMA and MPEG-PCL for controlled doxorubicin release.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Jun 1;178:56-65. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.02.043. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 30826554
Cited by
-
Using Amphiphilic Polymer Micelles as the Templates of Antisolvent Crystallization to Produce Drug Nanocrystals.ACS Omega. 2022 Jun 7;7(24):21000-21013. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01792. eCollection 2022 Jun 21. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35755329 Free PMC article.
-
Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery, Imaging, and Theragnosis.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jun 22;12(6):1397. doi: 10.3390/polym12061397. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32580366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mixed Pluronic-Cremophor Polymeric Micelles as Nanocarriers for Poorly Soluble Antibiotics-The Influence on the Antibacterial Activity.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Mar 24;13(4):435. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13040435. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33804932 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Understanding From Molecular Dynamics Simulation in Pharmaceutical Research 1: Drug Delivery.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Nov 25;7:604770. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.604770. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33330633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Application of ATRP in the Synthesis of Drug Delivery Systems.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;15(5):1234. doi: 10.3390/polym15051234. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904474 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Luo Y.L., Chen L.L., Miao Y., Xu F. Novel AB4-Type CTBN-b-MPEG PU Micelle-like Amphiphilic Block Copolymer Micelles for Prednisone Drug Release. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013;52:1571–1580. doi: 10.1021/ie3024164. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 21676058, 21808039, 21506038 and 21706039/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2016A030313694, 2016A030307043, 2017A030310300, 2018A030310525/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- DWYYTK-18KF001/Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Animal Nutritional Regulation
- 2017KZDXM076/Guangdong Province Education Bureau
- ZY0028/Cooperation project with Fujian Beisida Biology Co., Ltd.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

