Nanomaterials Designed for Antiviral Drug Delivery Transport across Biological Barriers
- PMID: 32085535
- PMCID: PMC7076512
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12020171
Nanomaterials Designed for Antiviral Drug Delivery Transport across Biological Barriers
Abstract
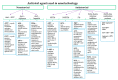
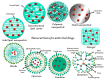
Viral infections are a major global health problem, representing a significant cause of mortality with an unfavorable continuously amplified socio-economic impact. The increased drug resistance and constant viral replication have been the trigger for important studies regarding the use of nanotechnology in antiviral therapies. Nanomaterials offer unique physico-chemical properties that have linked benefits for drug delivery as ideal tools for viral treatment. Currently, different types of nanomaterials namely nanoparticles, liposomes, nanospheres, nanogels, nanosuspensions and nanoemulsions were studied either in vitro or in vivo for drug delivery of antiviral agents with prospects to be translated in clinical practice. This review highlights the drug delivery nanosystems incorporating the major antiviral classes and their transport across specific barriers at cellular and intracellular level. Important reflections on nanomedicines currently approved or undergoing investigations for the treatment of viral infections are also discussed. Finally, the authors present an overview on the requirements for the design of antiviral nanotherapeutics.
Keywords: antivirals; biological barriers; drug delivery; nanomaterials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. [(accessed on 27 November 2019)]; Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en.
-
- UNAIDS Global Statistics Report 2019. [(accessed on 27 November 2019)]; Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet.
-
- WHO Global Hepatits Report. [(accessed on 25 November 2019)];2017 Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources