Current Advances in Allosteric Modulation of Muscarinic Receptors
- PMID: 32085536
- PMCID: PMC7072599
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10020325
Current Advances in Allosteric Modulation of Muscarinic Receptors
Abstract
Allosteric modulators are ligands that bind to a site on the receptor that is spatially separated from the orthosteric binding site for the endogenous neurotransmitter. Allosteric modulators modulate the binding affinity, potency, and efficacy of orthosteric ligands. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors are prototypical allosterically-modulated G-protein-coupled receptors. They are a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of psychiatric, neurologic, and internal diseases like schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington disease, type 2 diabetes, or chronic pulmonary obstruction. Here, we reviewed the progress made during the last decade in our understanding of their mechanisms of binding, allosteric modulation, and in vivo actions in order to understand the translational impact of studying this important class of pharmacological agents. We overviewed newly developed allosteric modulators of muscarinic receptors as well as new spin-off ideas like bitopic ligands combining allosteric and orthosteric moieties and photo-switchable ligands based on bitopic agents.
Keywords: acetylcholine; allosteric modulation; muscarinic receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



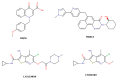
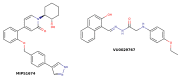



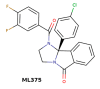
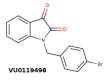
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

